What is Contextual Advertising and Why It Matters?
Last year Google announced that they will eliminate third-party cookies by the end of 2022. The industry is currently looking for privacy-safe alternatives to deliver highly personalized campaigns without relying on user data. This is when contextual advertising comes to the fore–a fully privacy-compliant technology with unique targeting capabilities.
But what’s the catch here for publishers, and should they adopt this method? Read along to find out!
What is Contextual Advertising?
Contextual advertising is a form of advertising that is contextually relevant to the page’s content. For example, a user might see a car ad while browsing a blog that writes about cars or a laptop ad on a tech review website.
Contextual advertising is powered by contextual targeting, a mechanism that matches ads to relevant sites using keywords. Contextual targeting is also used by search engines to display ads in search results based on the keywords used in the query.
Since targeting is a fundamental feature of online advertising, we will discuss the differences between contextual and behavioral (one of the most common targeting types) targeting further in the article.
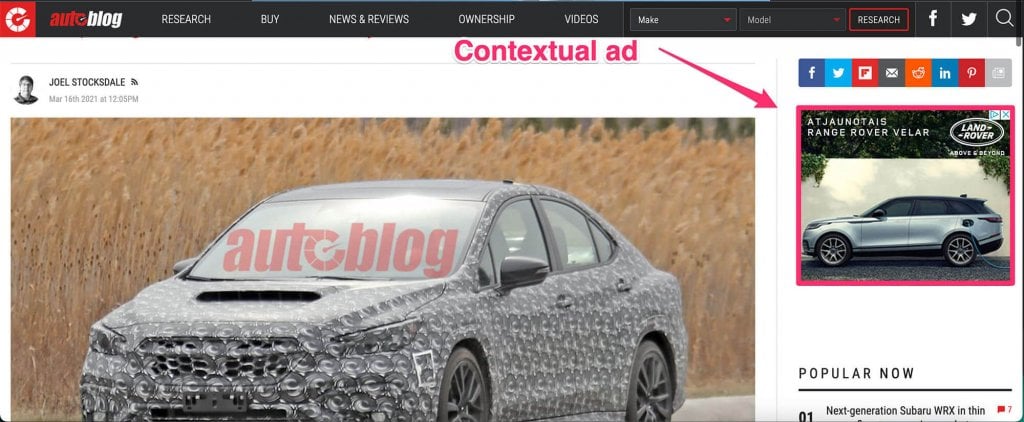
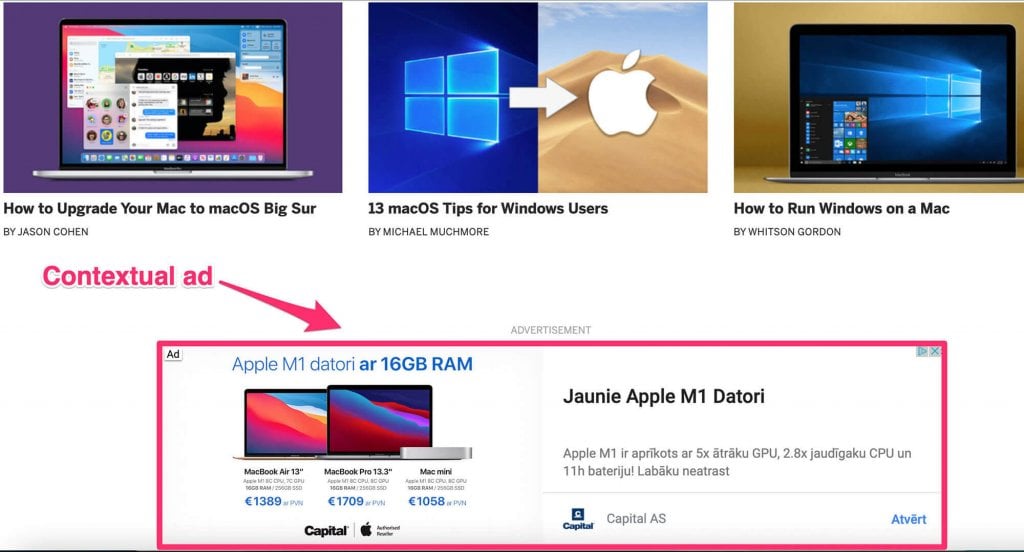
How Does Contextual Advertising Work?
The technology behind contextual advertising is very sophisticated today. For example, it can understand rich media such as pictures, video, audio, and even page quality.
It also utilizes semantic text analysis which is a process of interpreting text into its true meaning, with the ability to detect emotion, sentiment, and context.
How Does Contextual Targeting Work?
Simply put, contextual targeting happens on an ad network whereby the page’s content is matched with relevant ads based on keywords and topics. When a user visits the page, the ads are returned based on those keywords.
Moreover, the contextual approach offers ‘negative targeting capabilities’–an additional layer of precision around specific terms brands want to avoid. This has resolved long-standing issues related to brand safety when advertisers’ ads could appear next to inappropriate content.
Contextual Advertising Examples:
- Native Advertising
Native ads are a form of contextual advertising. They ‘blend’ into the webpage’s content because they appear where they fit most naturally. As a result, they mirror the website’s look and feel, for example, promoted search results or sponsored posts.
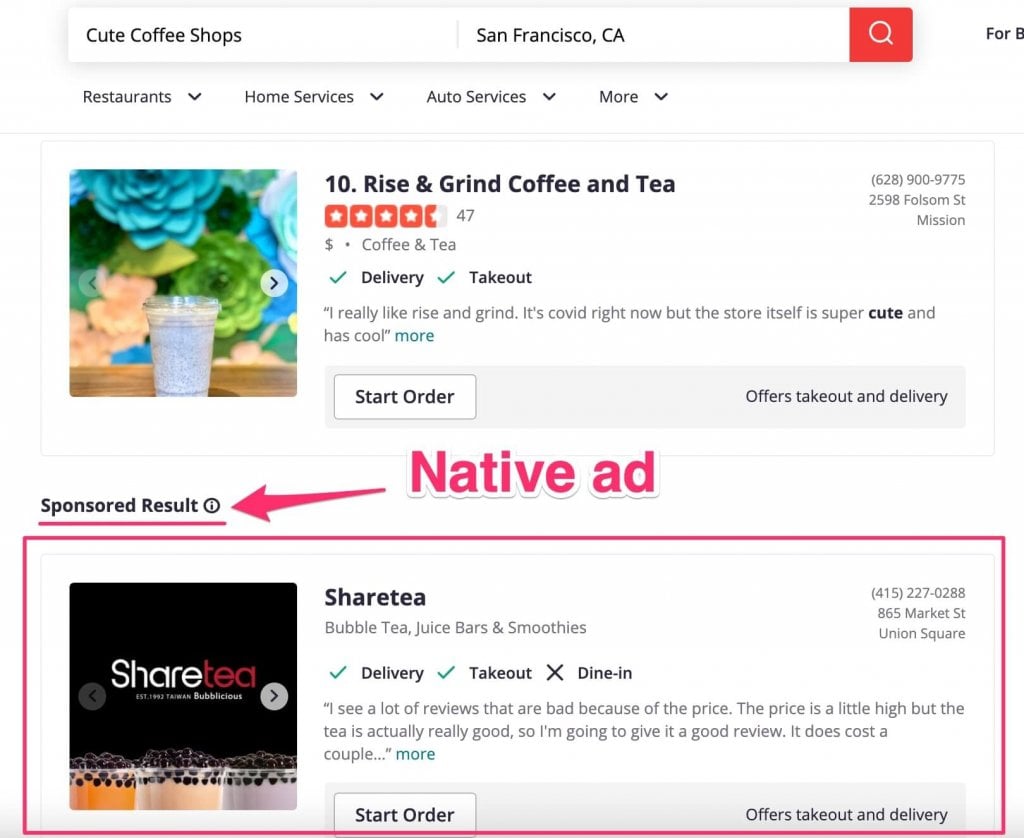
Related Article: Native Ads vs Display Ads
- Contextual Video Advertising
Video ads today can also be powered by contextual advertising technology. This technology analyzes the video’s sentiment and allows marketers to insert their ads at the best moment.
Instream video ads are relevant to the content being played in the video, which ensures that the viewer may find the advertisement relevant. In order to run instream video ads, publishers need to have video content and a video player on their page.
Publishers without video content can also monetize video ads on their page with outstream video ads.
Here contextual matching analyzes the publisher’s content and advertiser’s media and matches an ad with the relevant website. As a result, publishers can feature highly engaging, non-intrusive, privacy-compliant video ads on their website.
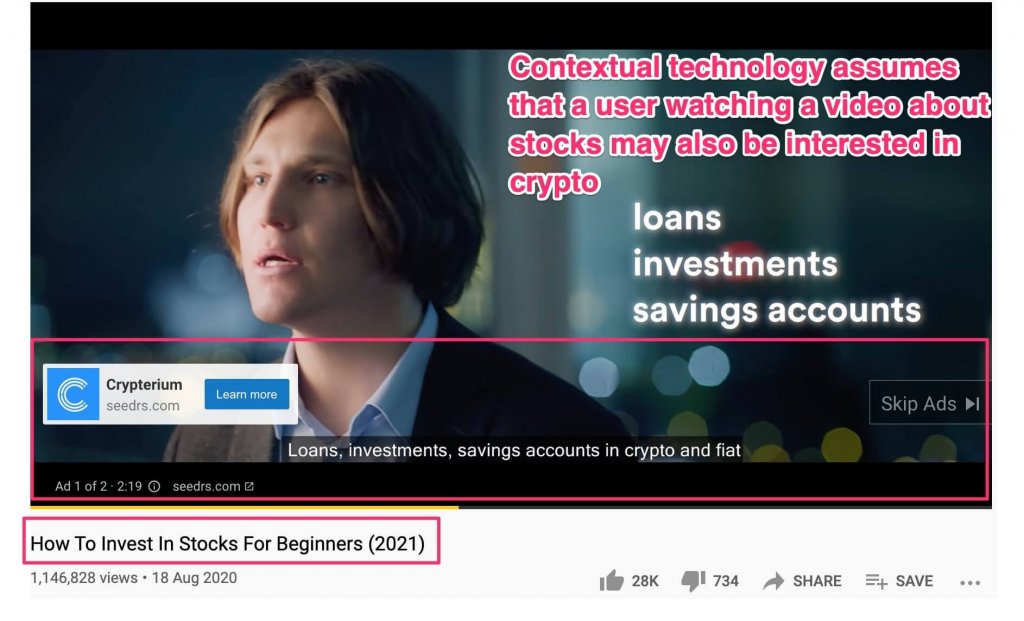
Related Article: Outstream Video Ads
If you’d like to know more about how to monetize instream and outstream video ads on your website, reach out to us!
Benefits of Contextual Advertising
- Privacy
Contextual ads are fully privacy-compliant and do not depend on cookies or other identifiers. Since privacy regulations become stricter and consumers demand more transparency over the use of their data, this means that publishers can monetize their ad inventory without any compliance issues.
- Better user experience
Contextual advertising is also better for user experience as users are seeing ads that are actually relevant to them.
- Data strategy
A shift from third-party to first-party data represents another opportunity for contextual advertising. According to an IAB survey, 57.1% of marketers from North America already had increased use of first-party and/or contextual data for targeting.
Likewise, brands will carefully leverage their first-party and contextual targeting capabilities, which will allow publishers to forge long-term partnerships with advertisers.
- Fairness
Advertisers historically favored large well-known publishers over small ones. However, as the industry shifts towards contextual advertising, there will be a chance to reduce this unfair advantage. According to a study, contextual intelligence emphasizes relevance and is unbiased towards larger publishers. At the end of the day, it’s the context that is important.
- Engagement
Contextually relevant ads create a more seamless and pleasant user experience, ultimately driving engagement. A study showed that contextual ads are 1.6x more memorable than non-contextual ads and 13% more engaging. Another study had found that visual media coupled with contextual targeting strategy generated 3.5 times better view quality results (a metric that looks at the length of time people spent watching the ad) compared with other display and video ads.
- Increased Revenue
Contextual algorithms favor high-quality, long-form content. This means publishers will enjoy increased revenue in the long run. This is also seen in advertisers’ incentive to increase their spending on contextual advertising.

Source: The Drum Studios; GumGum
Contextual vs Behavioral Targeting
People often confuse contextual and behavioral targeting. The main similarity of these methods is that they both use intelligence to display ads to relevant audiences. However, they are not the same.
Behavioral targeting is a process of displaying ads based on user web browsing behavior (e.g., interests, purchases, pages visited, clicks, etc.). Unlike contextual targeting, which uses keywords and semantic text analysis, behavioral targeting depends on user data and utilizes cookies and tracking pixels.
| Contextual Targeting | Behavioral Targeting | |
| Data Privacy | Fully privacy-compliant | Requires user consent to use data |
| Targeting | Utilizes keywords and topics | Utilizes cookies and tracking pixels |
| Accuracy | Less accurate as ads are less specific | More accurate as ads are more specific |
| CPMs | Lower (~29% less) | Higher |
| Compatible with Header Bidding | Yes | Yes |
In fact, behavioral targeting has been considered the most efficient targeting method for some time. However, with recent advancements in contextual targeting and increased data privacy regulations, there is a big chance contextual advertising will become a viable alternative to behavioral.
The Future of Contextual Advertising
Indeed, brands are turning towards contextual advertising because of third-party cookies phaseout. However, industry experts agree that other factors are also driving the popularity of contextual advertising.
One of those factors is efficiency. Industry analysis indicates that contextual intelligence drives better results than behavioral analysis and is more effective in reaching audiences. It is also more brand-safe for both advertisers and publishers. A more accurate understanding of the text opens more opportunities for publishers whose content often got blocked because of keyword blacklisting.
The future of contextual advertising is very promising, and publishers will only benefit from it in the long run.



