What is Audience Segmentation? 8 Main Types and Tips
Audience segmentation transforms how businesses communicate with their diverse customer base. Long gone are the days of “one-size-fits-all” marketing. Now, the focus is on crafting personalized messages that resonate with specific audience groups based on their unique needs, preferences, and behaviors.
Simply put, audience segmentation helps to divide a larger audience into groups with common interests so that marketing campaigns reach and resonate with them more effectively.
Read further and learn more about audience segmentation, its different types, importance in the ad tech world, and its benefits and complexities that publishers might face!
What is Audience Segmentation?
Segmentation in marketing refers to dividing and organizing the audience into meaningful and manageable groups.
Audience segmentation is a technique marketers use to identify subgroups within the target audience to deliver more personalized messages and strengthen connections. These subgroups can be based on different categories, e.g., demographics, user behavior, geographics, etc.
In short, audience segmentation helps to match messages, content, products, and services based on the specific needs and preferences of the audience.
Why is Audience Segmentation Important?
Many marketers create and share a single message with their audience to save time. However, audience segmentation allows to organize users into smaller groups, so they receive content that resonates with them. Once the user feels like the message is written just for them, they’re more likely to be receptive and engage further.
You cannot communicate successfully with an audience if you know nothing about them. And a personalized, targeted approach is essential to manage ad spending effectively.
Additionally, audience segmentation can offer significant benefits if you’re a publisher or a website owner.
Here are the 5 main advantages for you:
- Improved content personalization. Publishers can tailor their content more effectively by understanding the specific interests, needs, and behaviors of different audience segments. Thus, they can create a more engaging and relevant user experience, increasing time spent on the site, improving engagement rates, and increasing loyalty.
- Enhanced ad targeting and revenue. Audience segmentation enables more precise ad targeting, making ads more relevant to each user. It’s a crucial factor that helps improve the user experience by reducing irrelevant ad exposure and increasing ads’ overall effectiveness.
- Increased conversion rates. Understanding different audience segments can lead to more effective CTAs, offers, and marketing messages. This tailored approach can significantly boost conversion rates, whether the goal is newsletter sign-ups, product purchases, or membership enrollments.
- Efficient resource allocation. Audience segmentation helps publishers identify which segments that are most valuable or have the most growth potential. This enables the allocation of budgets and resources, focusing on the segments likely to deliver the best ROI.
- Better user experience and satisfaction. As mentioned, showing content and ads that align with each segment’s specific interests and preferences significantly enhances the overall user experience. This way, users feel understood and valued, leading to higher satisfaction rates, increased loyalty, and more frequent visits.
How Can Audience Segmentation Enhance Your Inbound Marketing Efforts?
Inbound marketing helps to attract customers by creating content and experiences that resonate with the audience. It prioritizes content creation and information sharing rather than relying solely on ads to reach customers.
Audience segmentation helps to divide a broad customer base into smaller, more manageable groups based on specific characteristics. One of the main benefits is that this allows to engage and convert prospects into customers because of more personalized and relevant marketing campaigns.
Example case:
Imagine a company sells fitness apparel online. Its broad target market includes people of various ages, fitness levels, and interests.
Goal: The company wants to employ audience segmentation to optimize its marketing efforts and ensure a higher ROI.
| Main steps | Segment A | Segment B | Segment C |
| 1. Identify segments | Fitness enthusiasts aged 18-25, interested in high-intensity workout gear. | Middle-aged customers aged 40-55, looking for comfortable, versatile fitness clothing for moderate exercise. | Yoga and pilates practitioners of all ages interested in sustainable, flexible apparel. |
| 2. Create targeted content | Create high-energy social media ads featuring young athletes wearing their gear during intense workouts, emphasizing durability and performance. | Use email marketing to highlight products offering comfort, versatility, and support for various activities, including walking and light jogging, accompanied by testimonials from customers of the same age group. | Focus on the sustainability and flexibility of their yoga line, utilizing blog posts and Instagram stories to showcase the eco-friendly materials and the comfort of their clothing during various yoga poses. |
| 3. Deliver content | Content is pushed through platforms popular with younger audiences, such as Instagram and TikTok, when they’re most active, like early evenings and weekends. | Email campaigns are sent in the early morning, offering inspiration for starting their day actively. | Targeted ads and posts are shared on platforms like Instagram and Pinterest, emphasizing the yoga line’s mindfulness and sustainability aspects. |
Outcome
By tailoring these marketing efforts to the needs and preferences of each segment, the company ensures that:
- Each segment sees messages that resonate with their specific interests and needs.
- The content is delivered on platforms where each audience segment spends their time.
- Messages are sent when each segment is most likely to be online and engaged.
This targeted approach makes the marketing message more relevant and engaging, significantly increasing the chances of conversion. It optimizes the company’s marketing spend by focusing efforts where they are most likely to yield returns, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of their inbound marketing strategy and improving their ROI.
Audience Segmentation Types
1. Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation identifies the audience based on age, gender, marital status, family size, income, etc. It’s one of the primary and most commonly used audience segmentation methods.
One of the easiest ways to adopt demographic segmentation is by using factors like age, gender, and income. However, there are other non-character traits that you can focus on.
For example:
- Income and family size are particularly useful segments for retailers, allowing them to single out certain groups interested in purchasing a specific product or service.
- Business-to-business (B2B) marketers are much more likely to rely on occupational segmentation to pitch their products to those who purchase for their company.
2. Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation groups users according to their interaction with your website or app. Marketers observe such aspects as readiness to buy, i.e., their knowledge about the product, level of loyalty, interactions with your brand or product usage experience, etc.
Simply put, behavioral segmentation divides customers into groups based on how they interact with a business or website.
The main aspects analyzed in behavioral targeting are:
- Customer opinion of your product or service (how they use it?)
- Customer knowledge about your company and its products as a whole.
- Customer buying habits, e.g., buying only on specific days like holidays, etc.
Note: Marketing campaigns that use behavioral data in addition to standard demographic and geographic segmentation methods can be more successful.
3. Psychographic or attitudinal segmentation
Psychographic segmentation divides users into segments based on their beliefs, values, lifestyle, social status, activities, interests, opinions, and other psychological criteria.
By analyzing motivations behind behaviors, psychographic segmentation helps businesses to build a better understanding of their target audience. Some businesses use psychographic data to develop products and services that resonate more deeply with specific audience segments.
- For example, creating separate segments for the audience based on whether they’re family-oriented or individualistic, adventure seekers or homebodies, leaders or followers, etc.
The attitudes, values, and needs central to psychographic segmentation are deep-rooted and take longer to evolve. That’s why this method can have a longer shelf life than behavioral and demographic segmentation.
It’s important to note that collecting reliable psychographic data can be challenging.
4. Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation divides the audience based on geographic location, from country to zip code. It enables targeting products, services, or marketing messages at people who live in, work in, or shop at a particular location.
By using geographic data, marketers can assess the market’s potential within a particular region, fine-tune distribution strategies, and tap into regional trends and consumer preferences.
- For example, geographic segmentation might utilize IP addresses to differentiate marketing strategies by country.
While geographic segmentation has its benefits, it also has some drawbacks.
For example, it can assume that people in the same geographical area have the same needs and interests, which isn’t always true. Cultural preferences and the complexities of consumer behavior can vary significantly even within the same geographic region, leading to potential oversights and inefficient resource use if used in isolation.
Relying only on geography for market segmentation could lead to missed opportunities and wasted resources.
While geographic segmentation offers a basic understanding of “where” your audience is, it falls short of explaining “why” they behave in specific ways. That’s where more in-depth approaches, such as psychographic segmentation, come into play–to provide a deeper dive into the motivations behind consumer behavior.
Thus, while geographic segmentation can be a useful tool, it should be combined with other segmentation methods for a better understanding.
5. Technographic segmentation
Technographic segmentation divides users based on the tools and technology they use. Typically customer segments from technographic data use factors like:
- Device type (e.g., smartphones, tablets, laptops)
- Software usage (e.g., operating systems)
- Application type (e.g., CRM software, web analytics tools)
- Cloud services (e.g., data storage, management)
- Social media consumption (e.g., Facebook, Instagram)
- E-commerce activities (e.g., online shopping, transactions)
Note: technography is a term created by combining two words–technology and demography.
6. Firmographic segmentation
Firmographic segmentation classifies B2B customers based on shared company or organization attributes. This segmentation approach helps B2B marketers properly position their products and services to their ideal market.
Firmographic segmentation variables include a business description, financial performance, and industry insights as major categories.
7. Needs-based segmentation
As the name suggests, need-based segmentation groups the audience based on their shared needs. Segmenting customers based on their needs makes it easier for marketers to tailor their messages so that all customers feel appreciated and understood.
Customer needs indicate why they buy a specific product or service. Once you identify a common need, you can understand why your customers make certain buying decisions. If you don’t understand your customers, the strategies to achieve your business goals may be threatened.
8. Value-based segmentation
Value-based segmentation evaluates the audience based on the revenue they generate and the costs of establishing and maintaining relationships with them. This segmentation strategy is made on the belief that some customers are more profitable than others.
It’s often used in eCommerce and entails identifying high-value clients by looking at customer data such as purchase history, frequency of purchases, average order value, and engagement indicators. With this information, personalized marketing offers and messages are sent to these customers to gain their loyalty and persuade them to make additional purchases.
Which Audience Segmentation Types are Most Useful to Publishers?
There are 4 main types of audience segmentation methods–demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral. However, demographic segmentation is one of the easiest and most commonly used.
Publishers find behavioral, demographic, geographic, psychographic, and technographic segmentation the most useful. Why? Here are some examples:
- Behavioral segmentation enables personalized content recommendations based on user interactions.
- Demographic segmentation tailors content to specific age, gender, and income groups.
- Geographic segmentation is key for targeting content to local or regional audiences.
- Psychographic segmentation allows for aligning content with the lifestyle and values of readers.
- Technographic segmentation optimizes content delivery based on the devices and technology the audience uses.
Planning your Audience Segmentation Strategy
An effective audience segmentation strategy involves a structured approach that starts with clear planning and understanding of your audience.
We’ve gathered the 6 main steps you should go through to perform your audience segmentation properly:
1. Plan your audience segmentation strategy
Begin with a clear understanding of what you want to achieve through segmentation. Your goals will guide your segmentation efforts, whether you’re increasing engagement, boosting subscriptions, personalizing content, or enhancing ad revenues.
Evaluate the tools, data, and resources you have available for segmenting your audience. These might include analytics platforms, CRM software, and audience data sources.
2. Set clear goals
Your goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- For example, increasing engagement among 18-25 year-olds by 20% in the next quarter.
Ensure that your segmentation strategy goals align with your general business goals (e.g., expanding into new markets or increasing overall user satisfaction).
3. Understand your audience
Use analytics tools, surveys, and social media interactions to gather data on your audience’s behaviors, preferences, and demographics. Then, analyze how different audience segments interact with your content to understand their preferences and pain points.
Based on this analysis, create detailed audience personas that represent the different segments within your audience.
4. Select the right segmentation criteria
For instance, consider user behavior and preferences if your goal is to personalize content. For geographic targeting, location will be your key aspect.
However, the most effective segmentation strategies often combine demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral data to create more accurate audience segments.
It’s important for you to test different segmentation criteria to see which yields the most meaningful insights and supports your goals. Always be prepared to refine your criteria based on what works and what doesn’t.
5. Implement your audience segmentation strategy
Once you’ve successfully planned your strategy and identified your audience segments, the next step is to implement targeted campaigns or content strategies for each segment. As mentioned, you should monitor performance to see how well your segmentation meets your goals.
Remember, effective audience segmentation is an ongoing process that requires continuous adjustment and optimization to stay aligned with audience behaviors and market trends.
How to Monitor and Analyze Audience Segment Performance?
One of the most important steps to effectively analyze audience segment performance is to monitor the most essential KPIs. This will help you to understand which segments are most valuable and responsive, allowing further improvement in marketing strategies.
Publishers should focus on KPIs that measure engagement, conversion, and customer behavior, such as:
- Conversion rates (how effectively segments lead to desired actions like purchases or sign-ups)
- Engagement rates (including time on site, page views, and interaction with content for each segment)
- Retention rates (how well different segments are retained over time)
- Acquisition cost per segment (cost-effectiveness of acquiring customers in each segment)
- Customer lifetime value (CLV) per segment (overall value a segment brings over their lifespan with the brand)
Another beneficial step is to find a comprehensive tool that will enable you to segment your audience easily. These tools should give you the opportunity to customize data so it can align with your needs and segmentation goals.
In this case, finding a trusted platform that specializes in audience segmentation could save you time and resources!
Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) provides an audience builder that allows you to create audience segments based on a combination of events, user properties, and other criteria. This enables website or app owners to receive more granular segmentation data that can be passed on to ad platforms for remarketing.
Additionally, since GA4 focuses on a unified user ID across devices and platforms, the segments more accurately track user behavior across multiple touchpoints
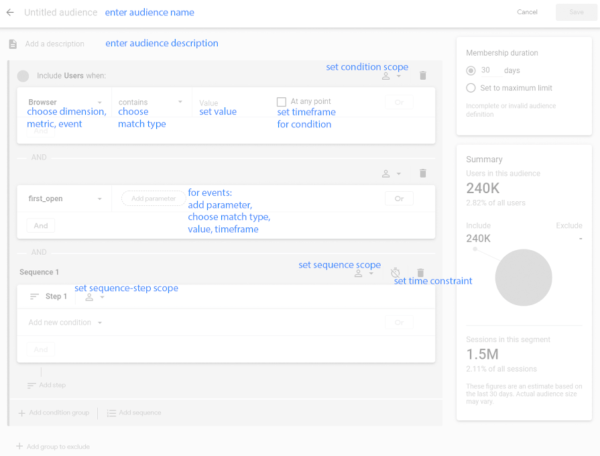
Source: Analytics Help
Important to note about GA4
Transitioning to GA4 from Universal Analytics involves a learning curve due to interface, reporting, and data model differences. It’s important to familiarize yourself with GA4’s features and capabilities.
If you’re migrating from Universal Analytics to GA4, ensure that you set up your tracking and event measurement to capture the necessary data for segmentation. This might involve configuring custom events and parameters in GA4.
Twilio Segment
Twilio Segment is a customer data platform that facilitates audience segmentation across multiple channels. It distinguishes itself as a platform built from the ground up for this specific task.
This platform offers data distribution, advanced segmentation recommendations, real-time analytics dashboards, unification into a single source for all customer data, and the ability to generate custom audience reports.
Additionally, its compatibility with over 300 data sources and destinations, including major advertising platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and LinkedIn Ads, ensures that publishers can easily integrate their existing marketing tools for a more coherent approach to audience segmentation.
Meltwater
Meltwater excels in finding patterns and connections within consumer data that businesses might not yet have discovered. It achieves this through a blend of real-time analysis across different data sources, giving a deeper understanding of customer behaviors and interests without requiring users to formulate precise queries.
Meltwater’s integration of established market research techniques, artificial intelligence, and expert data scientists sets it apart. It helps segment audiences effectively and provides clear interpretations of the value and implications of these segments, specifically aiding targeted engagement strategies.
Challenges in Audience Segmentation
Audience segmentation presents several challenges that can impact the effectiveness and efficiency of marketing strategies. Here are some of them:
- Collecting and analyzing audience data requires significant time and resources. Gathering insights through surveys, website analytics, and social media monitoring requires significant time and resources. Leveraging call center software can also streamline this process by providing detailed customer interaction data. This data is crucial for understanding audience behaviors and preferences, but it demands careful analysis to identify useful patterns and trends for segmentation.
Additionally, using more detailed demographic information, such as age, education, and employment, requires careful consideration due to privacy concerns and regulatory compliance, especially in regions with strict data protection laws like the European Union’s GDPR.
- The complexity of choosing an appropriate segmentation method. With various segmentation types available, selecting the right approach depends on aligning with business goals, understanding the audience, and leveraging the data at hand.
- The accuracy of targeting ads to segmented audiences. Since people’s interests and behaviors can change, targeting accuracy requires continuous updates and experimentation with segmentation methods.
- The cost associated with audience segmentation. The cost can be substantial, especially when involving large audiences or relying on third-party data. To manage costs, businesses are encouraged to use their own data as much as possible and explore cost-effective third-party solutions.
Conclusion
Audience segmentation is not merely an option but a necessity for crafting targeted and effective marketing campaigns that resonate deeply with different audience groups. It ensures that content and ads are not just seen but felt relevant and engaging by every audience segment.
However, challenges such as data collection, segmentation complexity, and associated costs can require substantial time and resources. Despite these hurdles, implementing an audience segmentation strategy can benefit publishers. It enables more targeted and effective marketing campaigns and ensures a more relevant and engaging user experience.
Thus, dedicating resources to refining and continually updating audience segmentation with precise, current data is not just a best practice but an investment in your business’s longevity and prosperity.
Ultimately, persistence in audience segmentation rewards publishers with increased revenue, user satisfaction, and loyalty.
FAQs
What is the difference between audience segmentation and market segmentation?
Audience segmentation divides your current and potential customers into specific groups based on personal attributes, while market segmentation categorizes the broader market, often including potential segments not currently served.
How often should audience segments be reviewed and updated?
Audience segments should be reviewed and updated regularly, at least once a quarter, to ensure they remain relevant and reflect current consumer behaviors and trends.
Can audience segmentation be applied to all types of businesses?
Yes, audience segmentation can be applied to all types of businesses, regardless of size or industry, to improve marketing effectiveness and customer satisfaction.
What are the first steps in creating an audience segmentation strategy?
The first steps in creating an audience segmentation strategy involve identifying your business goals, gathering and analyzing customer data, and defining segments based on shared characteristics relevant to those goals.
How can I ensure my data collection methods are compliant with privacy laws?
To ensure data collection methods comply with privacy laws, always obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting personal information, provide clear information about how you will use their data, and stay updated on and adhere to all relevant regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA.