How to Use Internal Links to Boost SEO | A Complete Guide
Internal links play an essential role in creating an enhanced and understandable website structure.
Internal linking improves the user experience, helps search engines to understand the site’s context, and increases page rankings.
In this article, you’ll learn why internal links are crucial to SEO and how to create an effective internal linking strategy for your website.
What is Internal Linking?
Internal links connect the site’s pages to one another in the same domain.
Internal linking helps navigate users through the website easily and creates a more definite site structure.
In other words, internal linking guides users throughout your website using a semantic SEO approach. This means that the internally linked pages are related in context to the article.
What is the difference between internal and external links?
The main difference between internal and external links is that internal links point users to different pages within your website. In contrast, external links point users outside your website to another site. Needless to say–both are important for SEO!
How to find internal links in a website?
There are 3 tips to find internal links on a website:
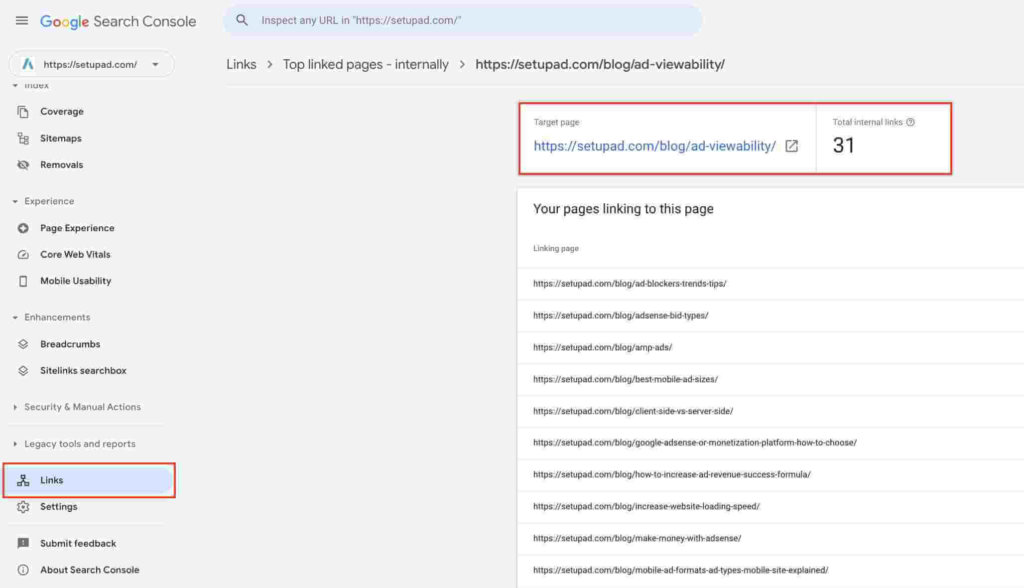
- Use Google Search Console. In the menu bar, press on “Links”, select or insert the website’s link, and you’ll be able to see all pages linking to your target page.
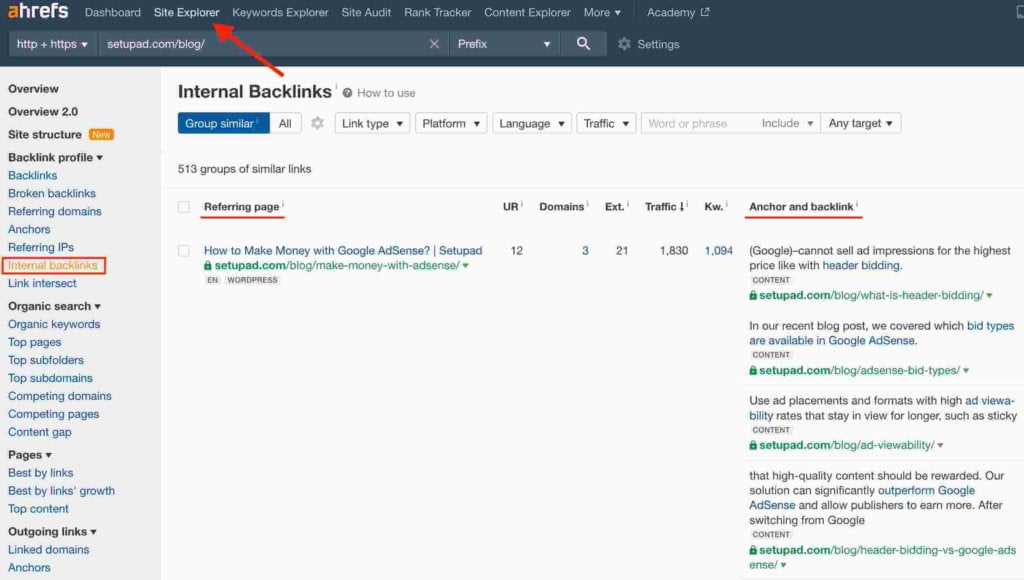
- Check internal backlinks on Ahrefs. Insert your domain link in the Site Explorer bar and then press on Internal Backlinks to see all pages linking to your referring page.
- Use a link explorer site like Moz Link Explorer.
Internal Link Example
Here is an internal link example with anchor text–the underlined, clickable text that guides you to a different page.
In this case, we’re using a related anchor text, which includes a variation of the target keyword. The anchor text displays “monetize websites with Google AdSense”.

By clicking on it, the user is redirected to another page in the same domain, further explaining how to make money with Google AdSense.

Types of Internal Links
There are 5 types of internal links:
- Navigational links–are made to navigate users throughout your website help them find what they’re looking for.
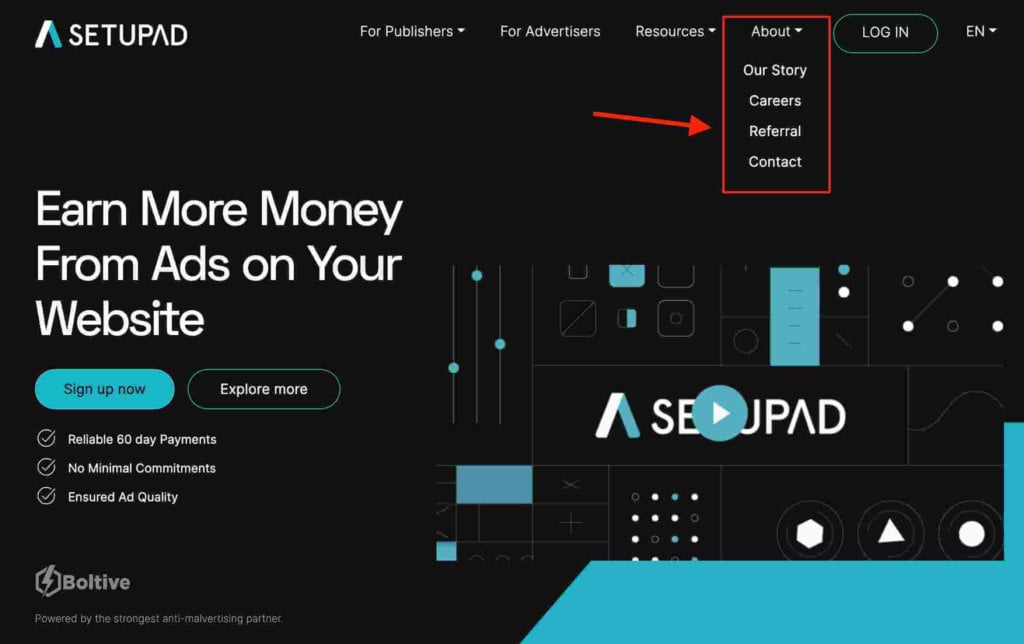
- Text links–are clickable texts in articles that usually link to another page with more in-depth information in relation to the text link. They are also known as “anchor texts”.

- Contextual links–provide links to additional resources.

- Image links–are represented as buttons, charts, and pictures that navigate the user to a related source.

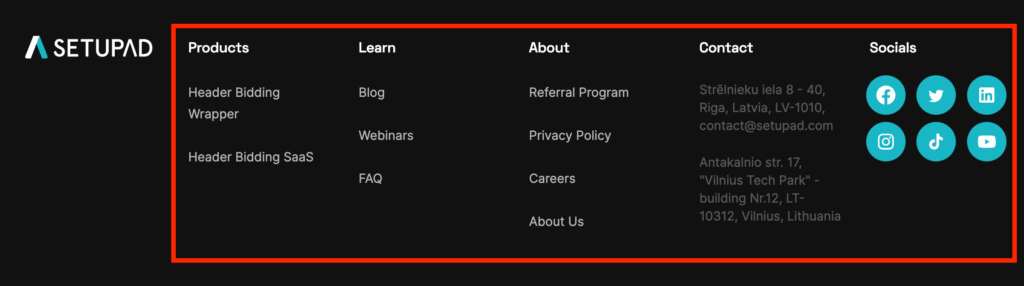
- Footer links–are usually located at the bottom of the page and contain links to social media, contact information, etc.
How Do Internal Links Work?
Internal links navigate users and search engines from one page to another within the same domain. They use a descriptive anchor text to demonstrate the relationship between these pages.
They work as a guide for the website, which eventually leads to every (if used properly) page on the site.
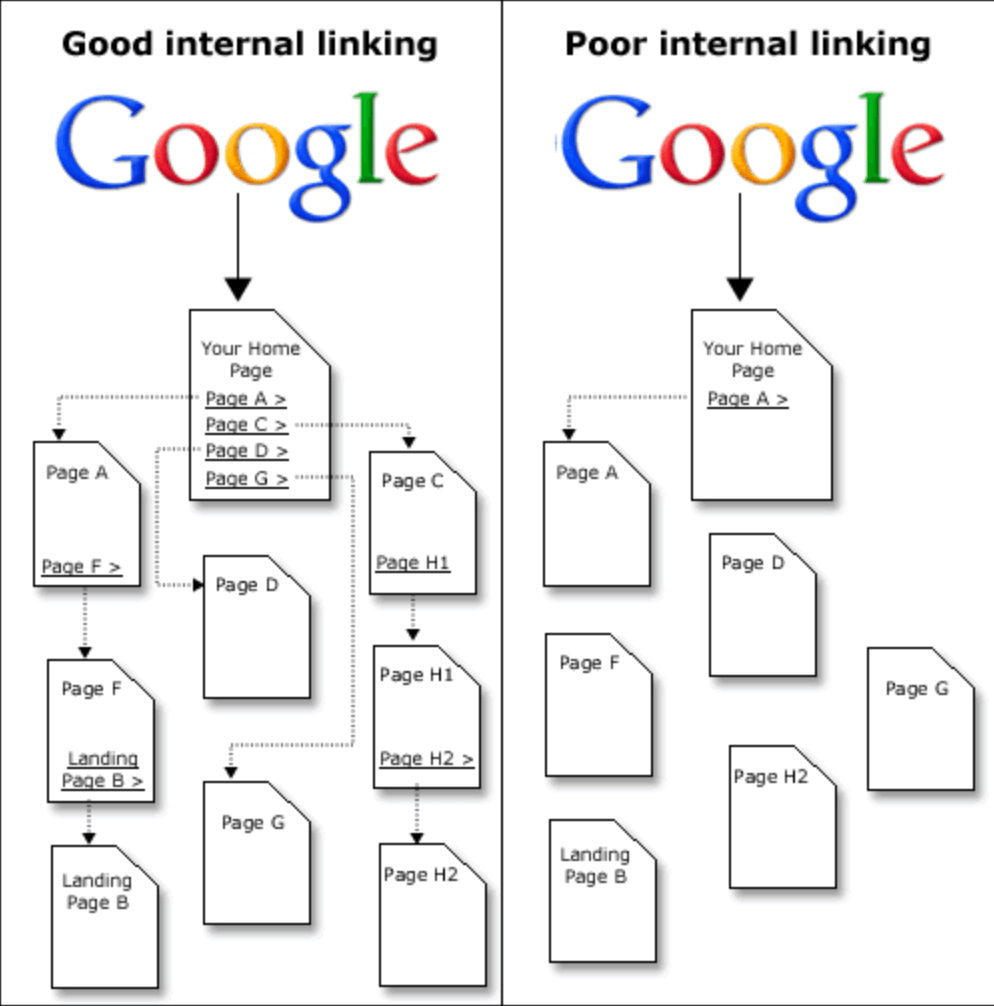
Internal link structure
Internal links help publishers create a site structure that organizes the content and provides a better user experience.
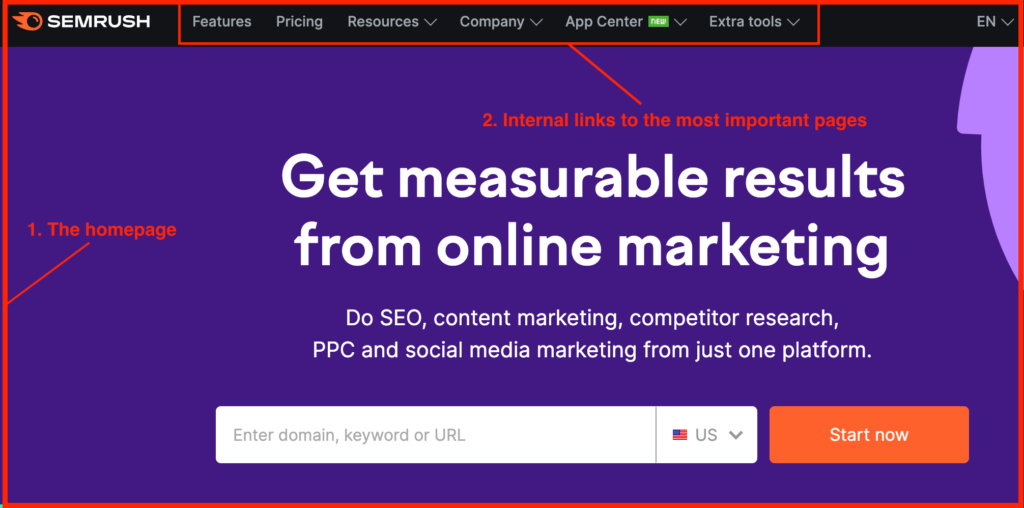
Internal links connect the website’s main homepage to the most important pages, which in turn connect to more pages that provide additional context.
Source: Reliablesoft
Internal links are like a map for the website. Without them, older content would be harder to discover by both users and search engines.
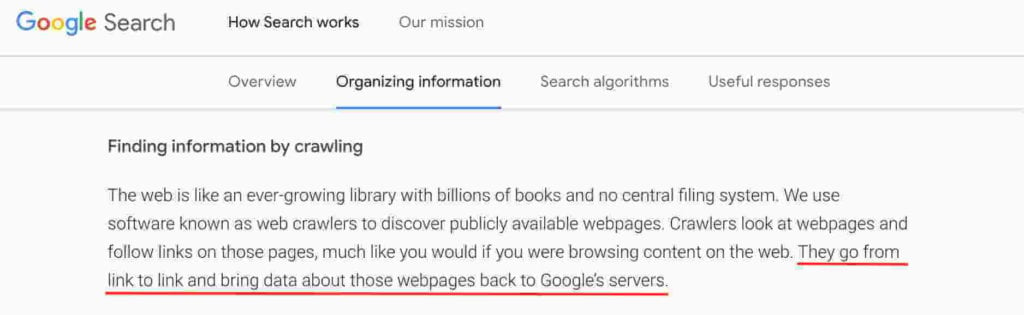
When search engines perform crawling and indexing, they start from the domain’s homepage and follow the links to other pages.
If you have a page that doesn’t link back to the homepage even through other pages, then search engines probably won’t discover it.
How Many Internal Links Should Be on a Page?
According to Moz, search engine crawlers have a limit of 150 links per page. This is a rough estimate because to learn the exact number, you must study the log files for each page. Therefore, a crawl budget can be bigger for a bigger page and smaller for a smaller page.

Source: Moz
Internal links should only be added where they’re relevant to the context. 5-10 links per 2000 words article is a good benchmark.
Nevertheless, it’s important to add internal links to new articles that link to older articles to improve their freshness.
Why is Internal Linking Important?
Internal links are the core of your website. And that sounds pretty important, right?
They help to understand the site’s structure, hierarchy, and context. The more internal links you’ll have pointed to a page, the more important it will seem to search engines.
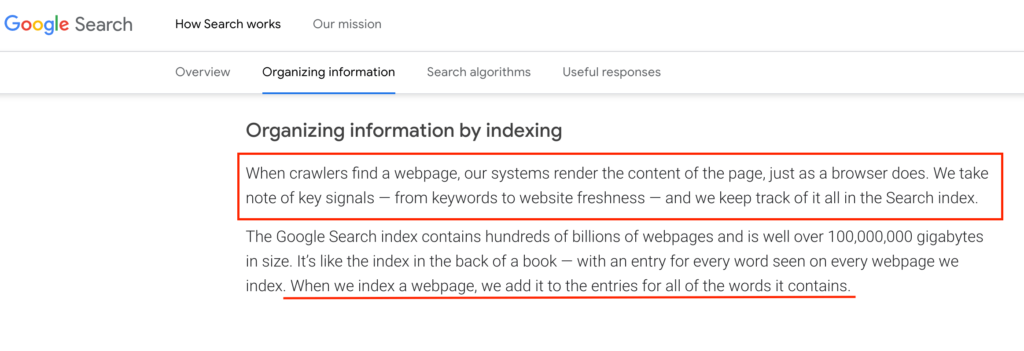
As mentioned, Google also uses internal links to better understand the site’s structure and relevance between the pages. It helps to understand the value and overall meaning of the page.
Google indexes important pages (the ones with the highest rankings and quality) on your website, but if too many pages exceed your crawl budget, some might be left behind.
Source: Google
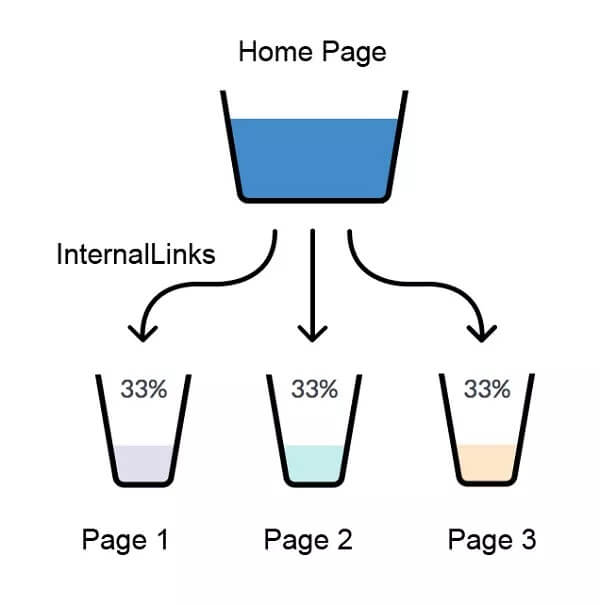
Internal links provide a more even distribution of “link juice” throughout the site. It determines the value and authority of pages and helps Google’s PageRank algorithm.
Source: Reliablesoft
PageRank is a system that ranks pages by measuring the quality and quantity of backlinks. Higher PageRank brings more authority to the site.
That means if you have a page with strong backlink profile, you can pass page authority to other pages by using internal links.
Benefits of Internal Linking
There are 5 key benefits of internal linking:
- Easy navigation. Internal links navigate users and search engines through the site in a logical and understandable way.
- Increased authority and link equity. Internal linking passes value and authority from one page to another, otherwise known as link equity or “link juice”.
- Improved page hierarchy. Internal links create a more distinct structure for your site. It helps search engines crawl through the website and find all the pages to understand their importance.
- Enhanced indexation of the site. Internal linking makes it easier for search engines to analyze the site’s content and meaning and find relevance between the pages.
- Better UX and engagement. If the site has a good structure, consistent navigation, and organized content, the user will spend more time on the page.
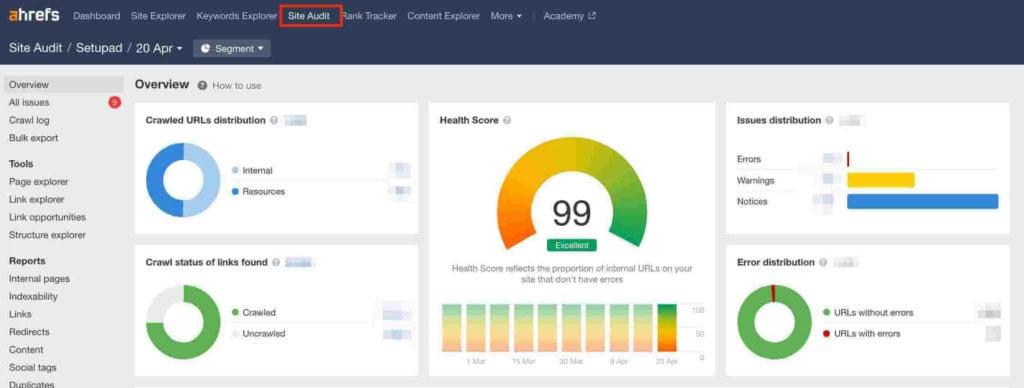
How to Audit Internal Links for Issues?
It’s important to regularly audit your internal links to avoid page performance issues.
If there is an issue with the page, it could be the fault of the page itself (e.g., no HTTPs protocol, high page latency, etc.) or there could be an internal linking problem.
To audit internal links for issues, you should:
- Plan your website’s structure and stick to it. Internal links are beneficial if they link to relevant sources, not random, unrelated ones.
- Find and get rid of orphan pages. Those are the pages that didn’t get included in your website’s structure. Find a way to link them to your content or remove them.
- Keep an eye on your internal no-follow links. These are links that don’t pass any page authority. They can make the PageRank points disappear from your website, so if you don’t want to pass more authority to unimportant pages, it’s better to use fewer internal links than more no-follow links.
- Be careful with image links. If the image link has no alt text describing it, then search engines can’t understand the context of the link.
- Audit your website for broken links, redirects, and robot instructions. You can do that with a site audit tool, like Ahrefs.
Are Internal Links Good for SEO?
Yes!
Internal links are one of the most important components to creating an actionable SEO strategy and a good website structure.
SEO isn’t just about ranking at the top of Google. It’s also about providing a good user experience, which is a key part of Core Web Vitals.
To master it, you must learn how to create a website that is easily accessible, understandable and provides all the necessary information.
Internal links bring more engagement, page views, and value to your site.
How to Build an Internal Link Strategy for SEO?
Here are 6 steps to building an internal link strategy for SEO:
- Create topic clusters. They organize your site’s structure and make it easier for users and search engines to go through it.
- Keep in mind the site’s hierarchy. The homepage is your top page which should link to the most important pages on your site. The rest of the pages and articles should be organized in hierarchical order as well.
- Use relevant anchor text. It helps search engines to understand the context and connection of the main page to the linked page.
- Don’t forget about your old content. It’s important to link back to older articles and update them to keep them valuable over time.
- Don’t put too many internal links on one page. You should keep in mind that search engines have a crawl limit, as well as users have limited patience for every link they have to click.
- Take advantage of your most authoritative pages. As they have more value, you can pass the link equity to other relevant pages through internal linking. As long as it fits in the context!
Conclusion
Internal links are the core of a good website and an effective SEO strategy.
If used properly, they bring value to your website, users, and search engines. Additionally, they can help to improve the ranking and the authority of your new and old content.
Most importantly, you need to create a logical site structure and use internal links to support this structure. Make sure to incorporate the best internal linking practices mentioned in this post and let us know in the comments if it worked for you!


