5 Tips You Should Do If Google Rewrites Your Title Tags
In 2021, Google changed how it generates title tags for web pages. Title tags might not have an immediate effect on ranking algorithms, but they give the first impression about your content to users.
Title tags are the first thing users see when they browse the SERP, therefore they can impact the page’s CTR (click-through rate) and the overall number of page views, which can affect your ranking in the long run.
In this article, you will learn the top 5 tips on how to avoid Google rewriting your title tags, and make sure that they meet all the necessary standards!
Why is Google Changing My Title Tag?
On January 2021, Google introduced a new update to how they generate web titles, and according to a study by Zyppy, out of 81,000 pages, 61% had their title tags changed.

Source: Zyppy
Google wants to assure that all title tags give a clear impression of the page’s content to users, and the update is meant to improve the readability and accessibility of page titles in search results.
According to Google, title tags don’t always describe a page accurately. If title tags are misleading, they can harm the overall user experience with the page and increase bounce rates.
The main reasons why Google’s changing title tags are:
- they’re too long;
- they’re stuffed with keywords;
- they contain repetitive words;
- they lack context.
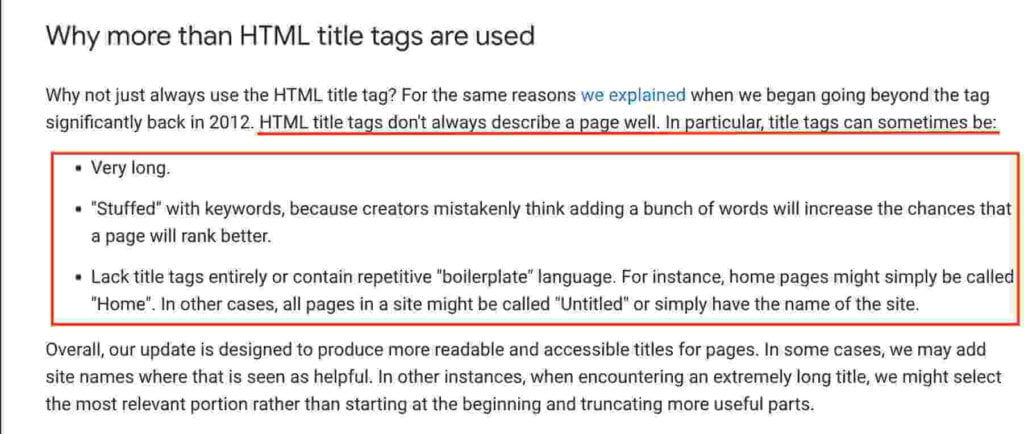
Source: Google Search Central
Where to see if Google has rewritten the title tags?
There are 2 ways you can check if Google has rewritten title tags:
- Use Ahrefs.
- Perform a site audit.
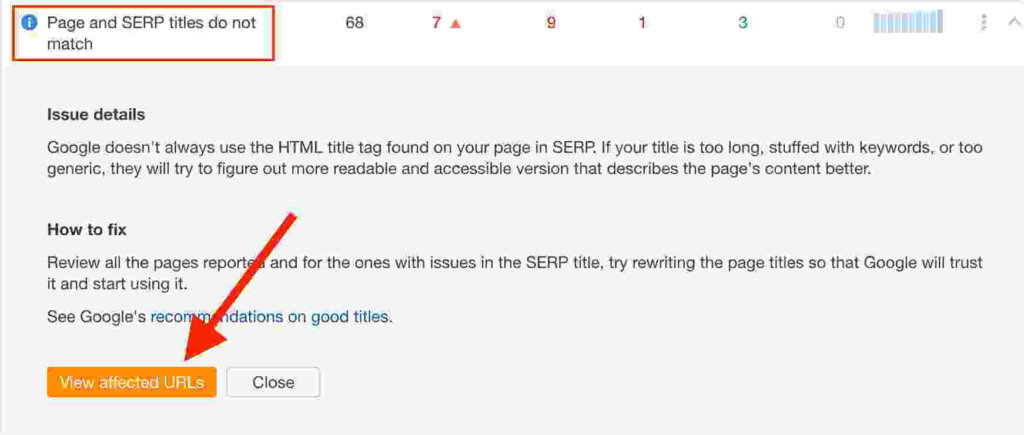
- Click on “Content” under the Reports section.
- Click on “Issues” and navigate to “Page and SERP titles do not match”.
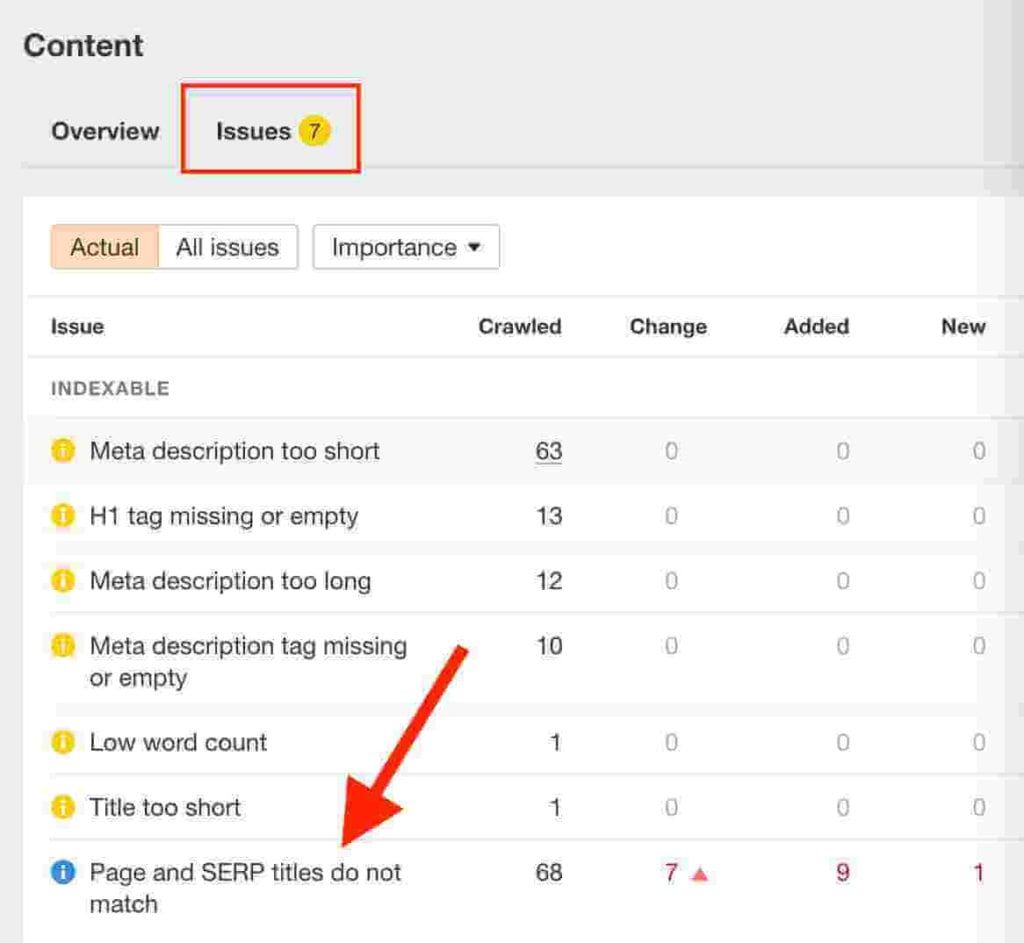
- Then click on “View affected URLs”.
- Use Google.
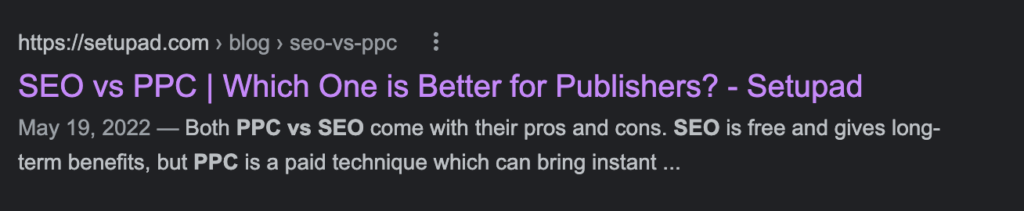
- Find the page you’d like to check in the SERP.
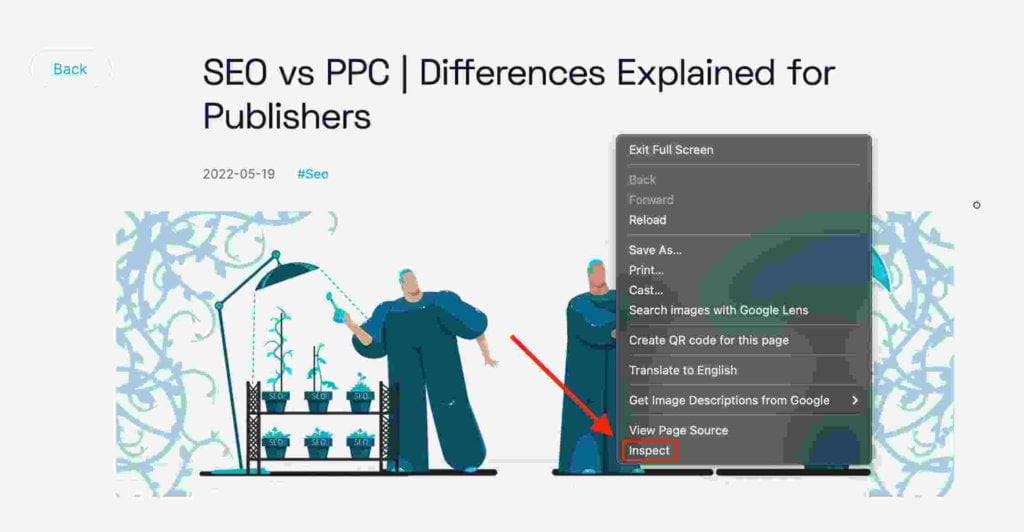
- Open the page, right click on your cursor, and choose “Inspect”.
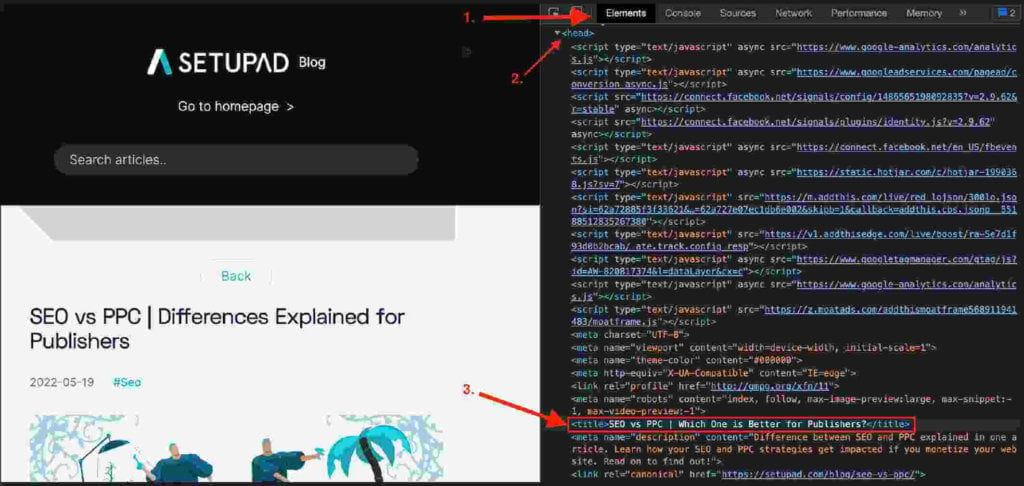
- Find the <title> in the HTML elements.
- Compare it to the SERP results to see if there are any differences made.
1. Check the Length of Your Title Tags
When Google rewrites title tags, they tend to become shorter than the original ones, which signals that you should keep your title tags concise. They should describe what your page is about in a short and simple way.

But remember, title tags need to match the context of your content. If title tags are too short or inaccurate, Google will find an alternative text from the page to add to the search results instead.
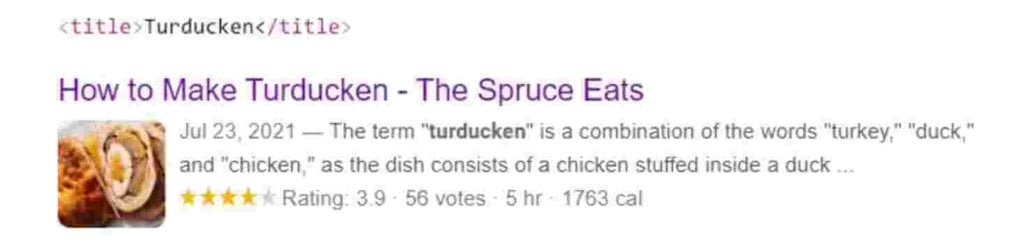
You should avoid using vague title tags like “Home” for the homepage because they don’t give any information about what you offer or who you are. Google tends to change these titles into brand or company names.

What will happen if the title tag is too long on Google search results?
If the title tag is too long, it might not fit in the search results. It can mislead users or drive away their attention to a different page, which has a more understandable and relevant title.
Keep in mind that title tags should be between 50-70 characters so they don’t appear cut off in the middle of the sentence.
2. Use the Correct Separation Signs for Title Tags
Separation signs like dashes “-”, “–” and the pipe “ | ” are commonly used nowadays to divide the title tag parts.
While there’s no real difference between them, with the new Google’s title tag update, it seems like Google has its own preference regarding them.
According to the Zyppy study mentioned above, title tags that had dashes were changed 19.7% of the time, but title tags that had the pipe as a separation sign were changed 41% of the time.
It’s clear that Google prefers dashes and other separator signs rather than pipes in title tags. Therefore, if you’re thinking which one to use–stick to dashes!
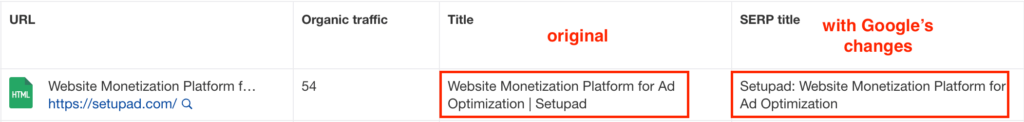
3. Try to Match the H1 to Title Tag
Google takes into consideration many HTML elements when changing title tags, but one of the most important ones is H1.
H1 stands for heading 1 (<h1>) and it defines the most important heading in your content. If you care about your site’s readability and structure, you should use this heading only once within your page.
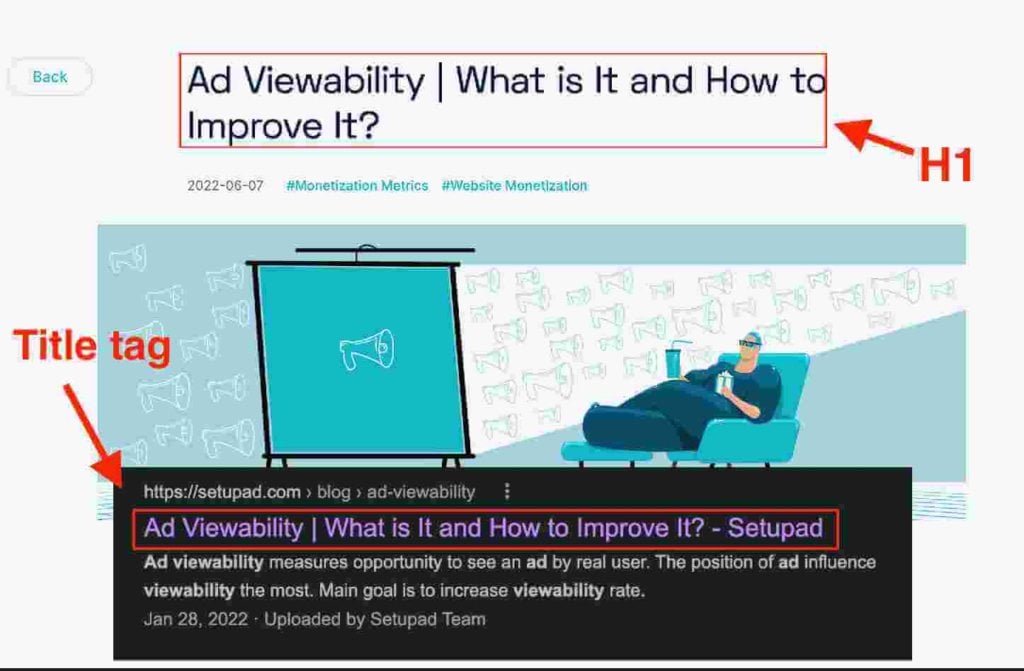
As H1 already highlights the main topic of your page, you should match it with your title tag. In fact, matching H1 with your title tag decreases the chance of Google rewriting it, because that’s the first thing it looks at when deciding to make changes in the title.
4. Write Content Based on Search Intent
Before you begin creating your content, you should analyze the user’s search intent regarding your main keyword to ensure you provide relevant information to the user’s query.
Most of the user’s search intent falls under 4 categories:
- Informational–the user wants to learn more about something (e.g., why should you monetize your website?)
- Navigational–the user wants to get to a specific website or a place (e.g., Facebook)
- Commercial–the user is researching the best product/service before interacting with it (e.g., best SEO tool)
- Transactional–the user is ready to make a purchase (e.g., buy plane tickets)
Typically, it’s easy to understand the user’s search intent by looking at the keywords used.
You can use Google Trends API to find the most relevant keywords that describe your content in the title tag to assure that your page matches the user’s search intent.
Another great SEO tip is to look at the first pages in SERP for your chosen keywords to see what kind of content they offer, as they are the ones that match the user’s search intent very well.
5. Avoid Keyword Stuffing
Keyword stuffing refers to a black-hat SEO technique in which a large amount of keywords are put into the content–visible text, backlink anchor text or meta tags (including title tags), in order to increase the chance of a better ranking position.
Search engines don’t approve this technique because filling content with irrelevant words results in a negative user experience. Therefore, the chance of damaging your ranking position is higher than improving it.
You should focus on relevant keywords and quality content. Writing rich, long-term content allows you to include and rank for more keywords naturally, and decreases the chance of getting penalized for keyword stuffing from search engines.
Conclusion
As a publisher, you know best what kind of content you offer on your pages. Therefore include relevant keywords and ensure that users also get a clear idea about your content from title tags.
Make sure that you follow our tips to avoid CTR drop and Google’s edits and improve the user experience on your page.
Have your title tags been affected by Google’s new update? Let us know in the comments!


