CPM Meaning – What is CPM in Marketing and Advertising?
CPM represents the revenue publishers earn for every thousand impressions that ads receive on their digital platforms. From another perspective, CPM measures the cost advertisers pay for every one thousand impressions their ads receive.
The CPM model allows publishers to capitalize on their site’s traffic by monetizing each view of an ad, ensuring a steady income stream based on the volume of audience engagement with the displayed ads.
This article explains CPM and explores its applications, benefits, and strategic importance in driving successful advertising outcomes.
What is CPM (Cost Per Mille)?
CPM is a fixed price advertisers bid or pay for each 1000 ad impressions. For publishers, CPM represents the revenue generated from these 1000 ad impressions. The CPM price is usually high if the website’s traffic is valuable, meaning advertisers will be willing to pay more for your ad impressions.
Publishers commonly use CPM to monitor the effectiveness of their display advertising sold through header bidding, AdSense, or other monetization platforms.
CPM Meaning
CPM stands for cost-per-mille or cost per thousand. The letter “M” in CPM comes from the Latin word “mille,” which means one thousand.
CPM vs. CPC vs. CPA: understanding the differences
| Description | Main benefits for publishers | |
| Cost per mille (CPM) | Advertisers pay for every thousand ad impressions on a publisher’s app or website | It’s best for high-traffic sites. CPM rates vary based on ad units, partners, geographies, formats, and devices. Provides a quick way for publishers to see how much they’re earning from impressions. |
| Cost per click (CPC) | Advertisers pay each time a user clicks on an ad. | Helps publishers understand revenue generated per click. Earnings depend on the number of clicks an ad receives. |
| Cost per acquisition (CPA) | Advertisers pay for each acquisition originating from an ad. | Allows publishers to optimize ad placements for conversions. Calculated by dividing total acquisition costs by the number of acquisitions. Highly valued by advertisers for its direct outcomes |
Understanding CTR (Click-Through Rate) and Its Role in Advertising
CTR, or Click-Through Rate, is a metric that measures the percentage of people who click on an ad after seeing it. It is calculated by dividing the number of clicks an ad receives by the number of impressions and multiplying by 100.
CTR = (Number of Clicks / Number of Impressions) x 100
A high CTR indicates that the ad is engaging and relevant to the audience, leading to more clicks. In the context of CPM, while CPM focuses on the cost or revenue per thousand impressions, CTR gives insight into how well those impressions convert into user interactions.
A high CTR can increase the overall effectiveness of a CPM campaign by ensuring that a higher proportion of ad impressions lead to clicks, making it a key metric in optimizing advertising strategies.
How to Calculate CPM?
The formula for CPM is the total cost of an ad campaign divided by the number of ad impressions and multiplied by 1000.
- CPM = total ad spend / number of impressions x 1000
For example, the publisher earns $1000 by selling 1M ad impressions. The calculated CPM would be $1. Thus, the publisher will earn $1 for every 1000 ad impressions he sells.
- (1000€ / 1M) x 1000 = 1€ (CPM)
How does CPM work?
Publishers use CPM to monetize their websites based on the number of impressions an ad receives.
Publishers charge advertisers a set fee for every thousand times their ad appears to viewers on the publisher’s site. This is especially beneficial for sites with high traffic, as it guarantees revenue for every thousand displays of the ad, regardless of whether users click on the ad.
Impressions vs. page views
Impressions and page views aren’t the same metrics. While impressions assess the reach of ads, page views focus on overall user engagement with the website.
- Impressions refer to the number of times a specific ad is served to a user.
Impressions track each instance an ad is loaded, thus providing a measure of ad exposure. A single webpage can have multiple impressions if it hosts several ads.
- Pageviews refer to the number of times a user views a page.
Each visit to the page is counted, regardless of whether the same user revisits or refreshes the page. This metric is crucial for understanding website traffic and gauging user interest in the site’s content.
What is a good CPM?
CPM isn’t a one-size-fits-all metric and varies significantly depending on numerous factors. What constitutes a “good” CPM for one publisher might not be the same for another. A good CPM is relative. You should evaluate it within the context of specific campaign objectives, target audience, and overall marketing strategy.
We suggest analyzing past campaign data, considering the target demographic and behavior, and continuously testing and adjusting strategies to optimize CPM relative to ROI.
Here’s a breakdown of what can influence the quality of a CPM and how you can determine if it’s good:
Market benchmarking – niche and audience quality
Understand the market averages for CPM in your specific niche. To gauge performance, you should look at industry benchmarks and compare their CPMs to similar sites or ad placements.
CPM rates can vary dramatically based on the website’s niche and the quality of the audience.
- For example, niches with high commercial intent, like financial news, may command higher CPMs due to advertiser demand for engaged audiences. In contrast, hobbies or entertainment niches may have lower CPMs.
Ad format and size
Advertisers are willing to pay more for ad formats and sizes that tend to perform better.
- For example, video ads often have higher CPMs than standard display ads because they engage users more effectively.
Additionally, ads that are more likely to be seen by users (those that appear “above the fold” or are in the user’s view longer) can bring higher CPMs.
Geographic location
CPMs also differ by geographic location, with advertisers typically willing to pay more for audiences in certain “tier 1” regions like the USA and UK, where the purchasing power is higher.
Ad network
Different ad networks can yield different CPMs.
Premium ad networks like Google AdSense tend to offer higher CPMs than others, reflecting the quality of ads and potential revenue for publishers. However, Setupad distinguishes itself with its cutting-edge technology, dedicated customer support, and a strong history of significantly increasing ad revenues compared to AdSense.
- For example, when publishers implement their recommendations, Setupad guarantees a minimum 30% increase in ad revenue over Google AdSense and Google Adx. Clients often see even more dramatic improvements, with some reporting increases of up to 300%.
Setupad encourages publishers to conduct a test run to provide a tailored estimate of potential results.
Return on investment (ROI)
Ultimately, a good CPM should make financial sense when considering the ROI. A campaign that yields a high CPM but does not convert to an equivalent or better return may not be valuable.
A lower CPM might indicate that while you’re reaching a large audience, it may not be the quality audience advertisers want. Conversely, a high CPM can be detrimental if it leads to a lot of unsold inventory.
CPM in Digital Marketing
CPM in Social Media Advertising
The profitability of social media advertising is nuanced.
Impression numbers have increased, indicating a higher viewership of ads, especially for formats like videos or stories. However, engagement with traditional ad formats is declining, as evidenced by reduced clicks and click-through rates.
This division in ad performance contributes to a split among global marketers regarding the measurability and clarity of social media marketing ROI.
The graph below shows that the average CPM rate dropped from $6.52 in 2022 to $6.06 in 2023. You can also notice that the CPM is higher in each year’s final quarter. This cost surge was prompted by increased demand for ad space, peaking during the year-end shopping season.
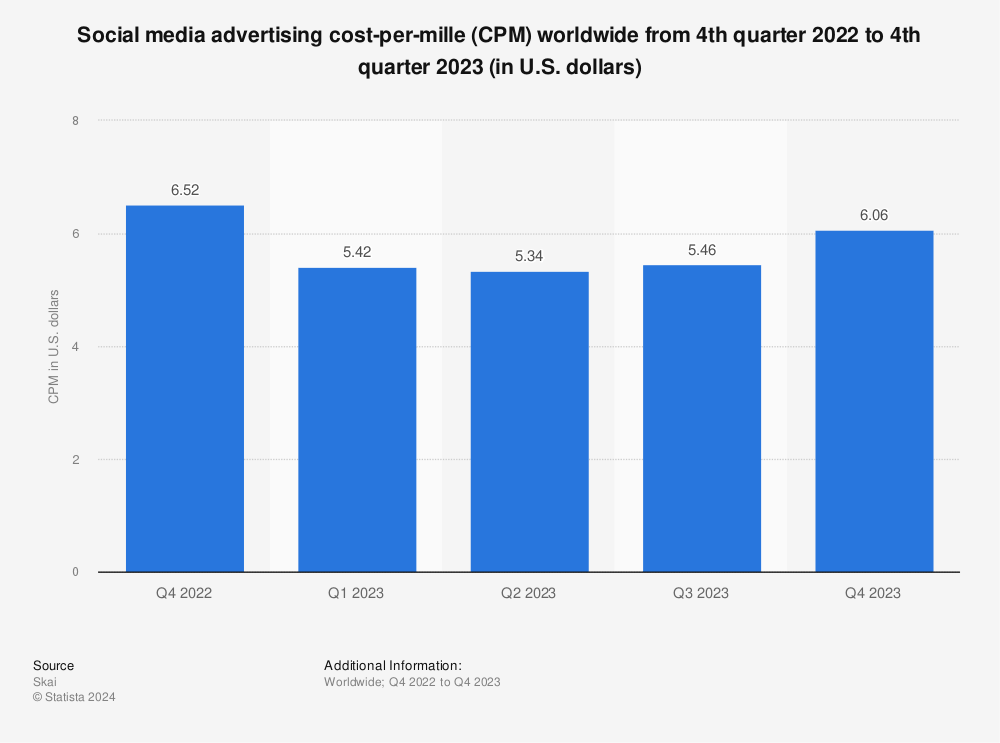
Source: Statista
Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Youtube, and Tiktok CPM rate in 2024
| Social Media Platform | Avg. CPM rate (2024) |
| Facebook & Instagram (Meta) | $6.63 |
| Twitter (X) | $2.53 |
| Youtube | $1.73 |
| TikTok | $3.37 |
Source: guptamedia
Strategies to Optimize CPM on Social Platforms
Optimizing CPM on social platforms helpts to maximize the ROI in ad campaigns. Here are 3 core strategies to achieve better CPM rates:
1. Refine targeting
Precisely define your target audience to ensure your ads are shown to the most relevant users.
Use the detailed targeting options available on social platforms, such as demographic data, interests, behaviors, and geographic locations. More accurate targeting can reduce wasted impressions and increase the relevance of your ads, which typically leads to higher engagement rates.
2. Improve ad creatives
High-quality, engaging ad creatives are fundamental in capturing users’ attention and fostering interaction. Invest in professional, appealing visuals and compelling copy that resonates with your target audience.
Experiment with different ad formats (e.g., videos, carousels, or static images) and run A/B tests to determine which creatives perform best.
3. Optimize posting times
Timing can significantly impact the effectiveness of your ads. Analyze when your target audience is most active on social platforms and schedule your ads to coincide with these peak times.
This ensures maximum ad visibility, potentially leading to increased engagement and a more favorable CPM. Use insights and analytics tools provided by social media platforms to refine and adjust the timing of your ads based on performance data.
CPM in Advertising
Display Advertising and CPM
Display advertising is closely intertwined with the CPM model, allowing publishers to monetize their ad space by earning revenue each time an ad reaches a thousand impressions. CPM focuses on the visibility of ads to a website’s audience.
Effective display ads grab user attention and can lead to actions such as clicking through to a landing page or revisiting the website, which is valuable for retargeting efforts.
User engagement influences CPM revenue. Thus, strategic ad placements are crucial. Ads positioned in high-visibility areas, combating banner blindness, and optimized for engagement can elevate CPM rates.
Programmatic Advertising and CPM
In the context of CPM, programmatic advertising’s automation ensures that the process is both time-efficient and scalable, adapting to the needs of advertisers and publishers alike.
Programmatic advertising combined with a CPM model offers publishers significant benefits.
For example, it increases revenue through competitive real-time bidding, often raising CPM rates. It enhances operational efficiency by automating the sale and placement of ads, reducing manual overhead. This system also optimizes ad inventory utilization, ensuring minimal unsold space, and provides targeted advertising based on sophisticated audience data, which can improve engagement and the value of ad spaces.
Additionally, publishers gain real-time insights enabling quick strategic adjustments, benefit from scalability as their traffic grows, and access a global advertiser base, expanding their monetization opportunities beyond local markets.
Automated buying and selling of ad space
Programmatic advertising automates the buying and selling of ad space, using software and algorithms to purchase display space efficiently. This process streamlines transactions, making them more cost-effective and strategically targeted.
Advantages and Shortcomings of CPM
Benefits of CPM
CPM advertising provides a range of advantages, but here are 5 most notable benefits:
1. Cost-efficient and measurable
CPM advertising allows publishers to monetize every impression their site generates. This can be more predictable and often more profitable than CPC or CPA models, as publishers are paid for exposure rather than actions.
Since CPM provides a wealth of data, publishers can monitor metrics like impressions, clicks, and conversion rates and use them to optimize their advertising strategy and improve ROI.
2. Increased brand awareness, reach, and visibility
For publishers with high-traffic websites, CPM campaigns can significantly boost the visibility of their brand or advertising partners. By reaching a broad audience, CPM helps drive brand recognition, which is crucial for new product launches or brand introductions.
Additionally, regular exposure through CPM campaigns can help publishers build trust and establish authority within their niche. The extensive exposure gained through CPM campaigns can contribute to a wider recognition of the publisher’s site, attracting more visitors and potential advertisers interested in leveraging that reach.
3. Perfect for video content
Given the popularity of video content, CPM is ideal for video ads such as pre-roll or in-stream, ensuring a vast audience sees them. This is particularly valuable as video ads often have higher engagement rates than standard display ads.
4. Transparent pricing
With CPM, publishers benefit from clear, straightforward pricing. They are paid a fixed amount for a set number of impressions, simplifying budgeting and financial tracking.
5. Scalability
CPM campaigns are easily scalable–publishers can adjust the number of impressions sold to advertisers based on demand and budget availability.
Cons of CPM
The main disadvantages of using CPM are rooted in its focus on impressions rather than actions, which may not always correlate with campaign objectives (e.g., conversions or sales).
Here are the 3 main shortcomings to consider:
1. Difficulty in detecting attribution
CPM is centered on the number of times an ad is displayed, not on the number of times it’s clicked or leads to a conversion. Thus, a high number of impressions doesn’t necessarily show a corresponding number of sales or inquiries.
CPM emphasizes the breadth of ad exposure but does not account for user engagement.
Impressions increase reach and can build awareness, but the impact on user behavior might be minimal without clicks or interactions.
Tracking the customer journey and attributing a conversion to a specific CPM-based ad exposure can be challenging. If a potential customer sees an ad but only acts on it days later, it’s hard to prove the ad was the reason for this action.
2. Ineffective targeting
There’s a risk that ads may be seen by users outside the target demographic, which can dilute the campaign’s effectiveness. Without the right targeting and measurement of engagement, CPM campaigns may result in ad spending that doesn’t contribute to the bottom line.
3. Ad fraud
Digital ad fraud is a significant concern in CPM campaigns. Bots can artificially inflate the number of ad impressions, leading advertisers to pay for views that are not performed by real people with genuine interest or intent.
How to Improve Your CPM?
Here are concise steps for publishers to improve their CPM:
- Produce high-quality content
Continuously offer engaging and relevant content to keep visitors returning. Keep an eye on how your website functions and if it retains a good user experience. Address issues with slow page loads and poor design, impacting site performance and visitor retention.
- Optimize price floors
Adjust your ad price floors regularly based on demand and industry trends. Lower the floor price when demand decreases to stay competitive and increase it when demand spikes to maximize revenue without pricing out potential buyers.
- Cultivate quality demand partnerships
Establish relationships with high-quality demand partners through direct deals or ad networks. Quality demand from partners who value your specific audience and content type can significantly increase your CPM.
- Experiment with ad units
During periods of low demand, test different ad units or configurations. Standard units often perform well, but exploring new options might capture additional interest and improve fill rates.
Additionally, you can enhance your ad landscape by adding new, user-friendly ad units. Ensure these units integrate seamlessly and do not detract from the user experience, aiming to increase site monetization without overwhelming users.
- Focus on SEO and Core Web Vitals
Invest in SEO to increase site visibility and traffic, which is vital for ad performance. Optimize your site with relevant keywords, fast loading times, and mobile-friendly design to improve search engine rankings.
Lastly, remember to meet the standards of Google’s Core Web Vitals, which influence search rankings. Enhance your site’s loading performance, interactivity, and visual stability to boost its presence in search results.
How can Setupad Help Improve Your Advertising CPM?
Setupad enhances publisher CPM rates by adopting a holistic approach that optimizes ad revenue and improves the overall website experience. This is achieved through strategic ad placements that boost viewability and user engagement, coupled with efforts to increase website traffic.
Setupad’s team, including Account Executives and AdOps managers, uses deep industry knowledge to ensure ads are seamlessly integrated, enhancing the value of the inventory without compromising the user experience.
This holistic strategy makes the publisher’s site more attractive to higher-paying advertisers. It aligns Setupad’s interests with its clients’ interests, driving mutual success through enhanced ad performance and elevated CPM rates.
The better the performance, the greater the demand for the publisher’s inventory.
Setupad’s track record of success showcases their commitment to helping publishers thrive. The case studies below highlight how Setupad effectively boosts revenue and enhances user experiences across diverse publishing platforms.
If you want to improve your advertising CPM, join a trusted monetization partner like Setupad and test our solution without risk!
Conclusion
The CPM model is a reliable way for publishers to monetize their content through impressions, enhance brand visibility, and reach large audiences. CPM allows publishers to generate steady revenue based on their site traffic by charging advertisers for every thousand times their ad appears.
It’s not a secret that effectively using CPM will continue to be crucial for publishers aiming to maximize their ad revenue and achieve sustainable growth.
Nonetheless, finding a trusted monetization partner is essential.
A good monetization partner will help to optimize CPM strategy, allowing publishers to focus on their core activities and less on the complexities of ad management.
FAQs
What Makes CPM Different from CPC and CPA?
CPM charges advertisers for every thousand impressions an ad receives. In contrast, CPC charges for each click on an ad, and CPA charges for specific user actions like purchases or sign-ups.
How Do I Know if My CPM is Good?
A good CPM is generally lower than industry averages but still drives significant traffic and awareness; assess it against campaign goals and ROI.
Can CPM Be Used for All Types of Advertising?
CPM is adaptable and can be used across various advertising forms. It’s especially effective for building brand awareness rather than immediate conversions.
How Can Small Businesses Leverage CPM Effectively?
Small businesses can use CPM to cost-effectively increase brand visibility and manage ad budgets, especially targeting specific demographics or interests.





