8 Key Steps to Recover From a Google Core Update
Have you ever wondered how Google brings the most relevant organic search results from your search query? Google uses a complex system of hundreds of different signals to retrieve data from its search index.
Ranking factors, such as target keywords, page relevancy, site authority, and many more, determine whether or not your website will appear on the first page of the SERPs (Search Engine Results Page).
Did you do a good job at optimizing your content and website for the search engine? Then your page will have a fighting chance to receive organic traffic from Google and climb rankings.
What is a Google Core Algorithm Update?
Google constantly updates and changes its search algorithm to provide the best possible search results. They say that they make small changes to the algorithm daily.
However, Google also releases a broad core algorithm update every couple of months, targeting a more extensive set of signals.
These changes are impactful enough to cause major disruption among publishers and bloggers.
Every time a new core algorithm update is released, the SERPs become very volatile for around two weeks (sometimes longer). As a result, some websites lose traffic and keywords, while others–gain them.
Google usually announces if they plan to release a new core update a few days before on their Twitter channel. However, they say it will take around one to two weeks for the update to roll out.
What types of Google updates are there?
There are 3 types of Google updates that we know about:
- Smaller updates that Google does every day, sometimes more than one update a day. The results of these updates aren’t noticeable right away.
- Named updates, like Penguin or Panda. These updates target specific problems in Google’s algorithm and happen infrequently. For example, the Penguin update in 2012 targeted spam issues dealing with manipulative backlinking practices. The Panda update, released in 2011, targeted low-quality websites with poor content.
- Broad core updates. These updates are released, on average, around 4 times a year. They don’t target a specific issue or problem. Instead, they’re released to improve the overall Google search algorithm.
How To Tell if Google Has Released a Core Update?
The quickest way to find out if Google is about to release a core update is to follow their Twitter channel. They usually announce the core update release a couple of days in advance.
However, if the update has already happened, there are other ways to tell.
One of the most visible indications is sudden volatility in search engine results pages.
There are also free tools out there to check that:
- Semrush Sensor shows real-time daily volatility data across various categories for free.
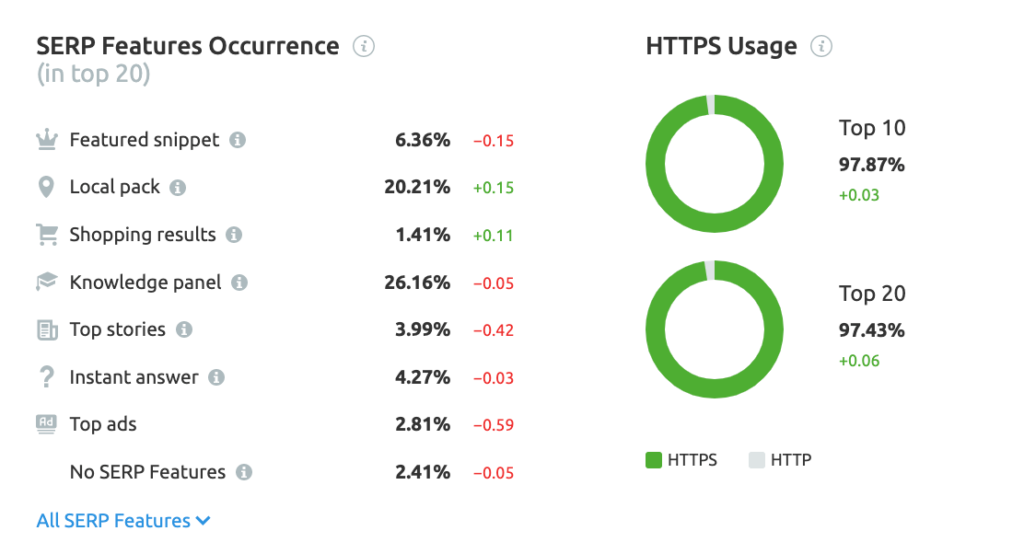
- Mozcast–provides a daily weather update of Google’s volatility. If SERPs undergo significant disruption, the conditions will increase and become more stormy.
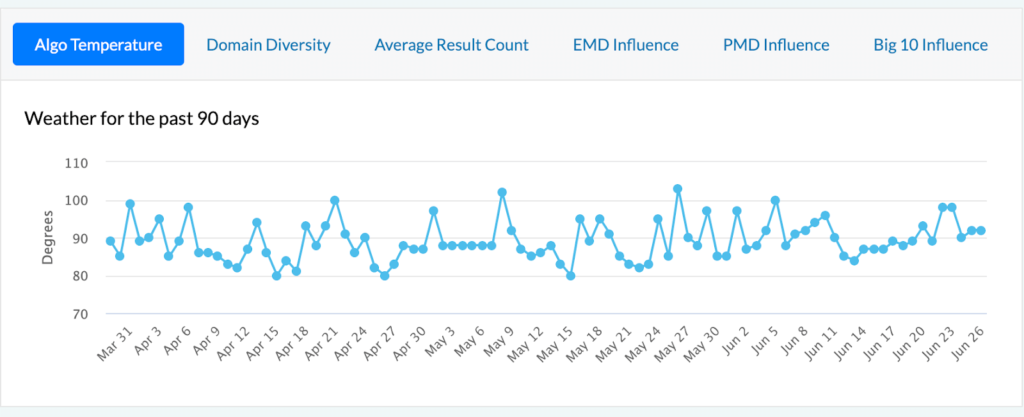
- Algoroo–provides an overview of changes and analyzes how it affects the SERPs.
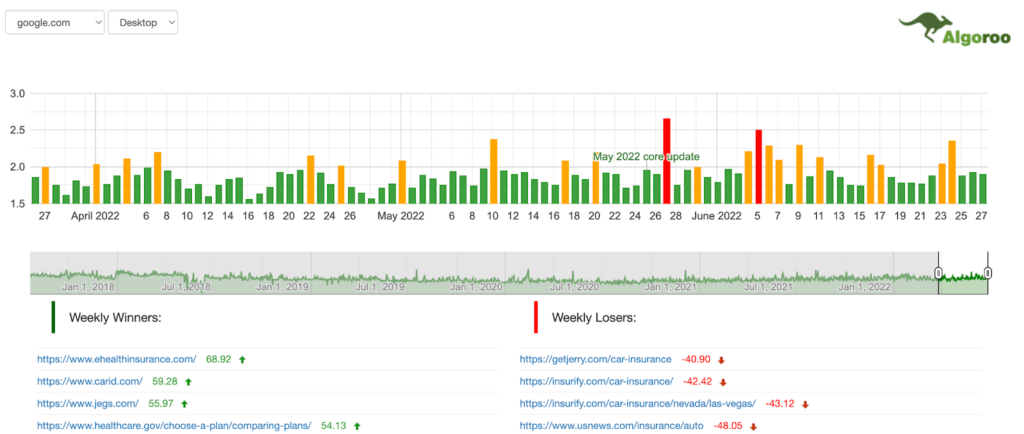
These tools require some understanding of SEO, but studying them is worth your while.
If you just want to know whether or not there has been a Google core update, you can check what the industry professionals are saying.
Forums, thought leader discussions, and SEO-news websites are great places to start:
- Search Engine Roundtable is an excellent source to quickly learn about any new core update that was released, like the May 2022 core update. In addition, they provide a brief description of the update and collect some chatter from SEOs on Twitter.
- Ahrefs compiles and briefly describes each core update, dating back to 2015. They provide readers with what they think was the main target of the update.
- Search Engine Journal also makes an announcement whenever a new Google core update is released, along with the general guidelines from Google on how to react to it.
- Authority Hackers cover this topic on their YouTube channel. They provide a deeper analysis of the update, their expertise, and thoughts on what it targets and how it affects the SERPs.
You can also check your website data in Google Search Console and Google Analytics to look for changes in your rankings, paying particular attention to CTR versus impressions.
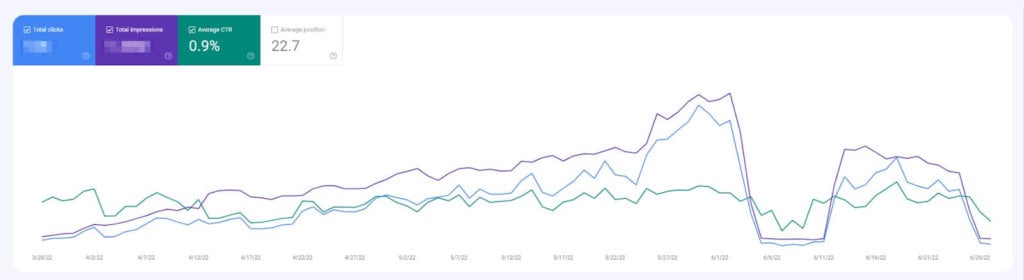
In the picture above, you can see that shortly after the May 2022 update, which began on May 25, both impressions and average CTR had seen a noticeable drop.
My Rankings Dropped Heavily–Any Chance They’ll Go Back?
First of all, you shouldn’t start making any changes the morning when you discover that there has been a Google update and you’ve lost a lot (or all) of traffic and keywords. It takes around three days for the update to make an impact.
But SERPs can remain highly volatile for a couple of weeks. During this time, the Google algorithm will assess all websites in their index to determine which provides the best search results.
So take time to evaluate what happened with you, your competitors, and websites in other niches.
SEO experts will jump on the update as soon as possible, often with a much larger data sample to work with. Their research, analysis, and hypothesis are worth waiting for.
Secondly, you likely won’t get your rankings back immediately after the update. Not even if you knew exactly what to do and implemented all the right changes and fixes.
Occasionally, a site that lost its traffic and keywords at the beginning of the core update rollout might see some improvement by the end of it.
That means that the update decided that your website brings a more relevant answer to the search query than your competitors.
What did the core update target?
Google doesn’t usually let publishers and blog owners know what aspects of the search algorithm it targets. So you should check Google’s guidelines on quality content creation and follow them.
Previous updates targeted different aspects of SERPs and search mechanics to combat things like slow page speeds, low-quality affiliate websites, spammy link-building methods, etc.
By analyzing the SERPs and listening to what the industry experts are saying, you can deduce what was the main target of the core update this time.
Once you have that information, you can act to make your website meet these new, updated criteria of the Google search algorithm.
For example, Ahrefs thinks that the May 2022 update targeted E-E-A-T, which analyzes and measures the value of your website’s main content.
First Step to Take After the Google Core Update
First, you need to do your research before you can start the recovery journey. Try to analyze what part of the Google algorithm was targeted with this update. To do that, it’s essential to understand which parts and types of pages on your website were affected.
Find out and compare which pages were affected the most traffic and impressions-wise and which pages lost the most average rank.
To check trends on how your website is doing, head to Google Analytics and navigate to Behavior → Site Content → All Pages. From there, you can see which pages lost or gained Page views, dwell time, bounce rate, and other metrics, as shown in the screenshot below.
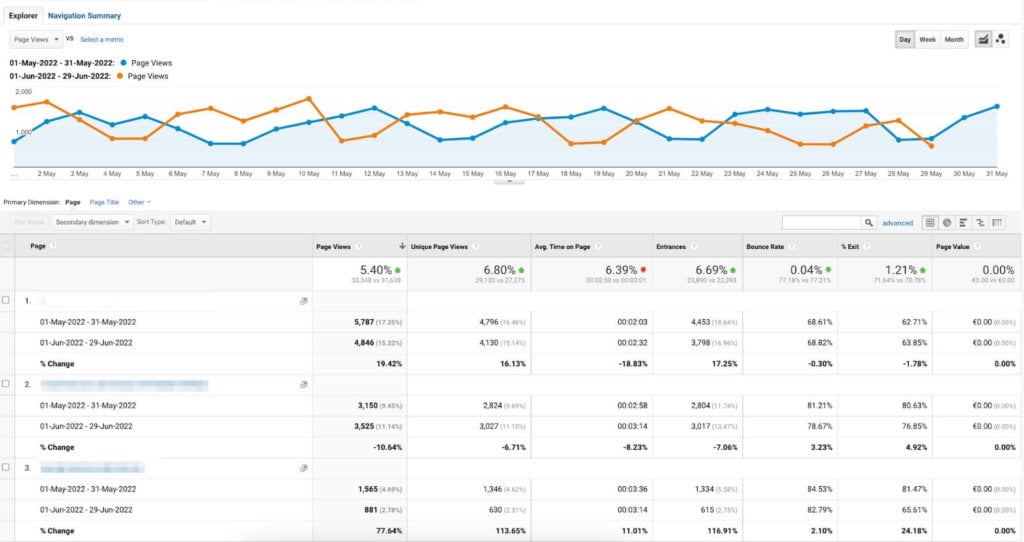
To check average page position changes, go to Google Search Console and navigate to Search Results. Next, check the “Average Position” box and switch the view to “Pages”. There you can play around with comparing different date ranges, as shown in the screenshot below.
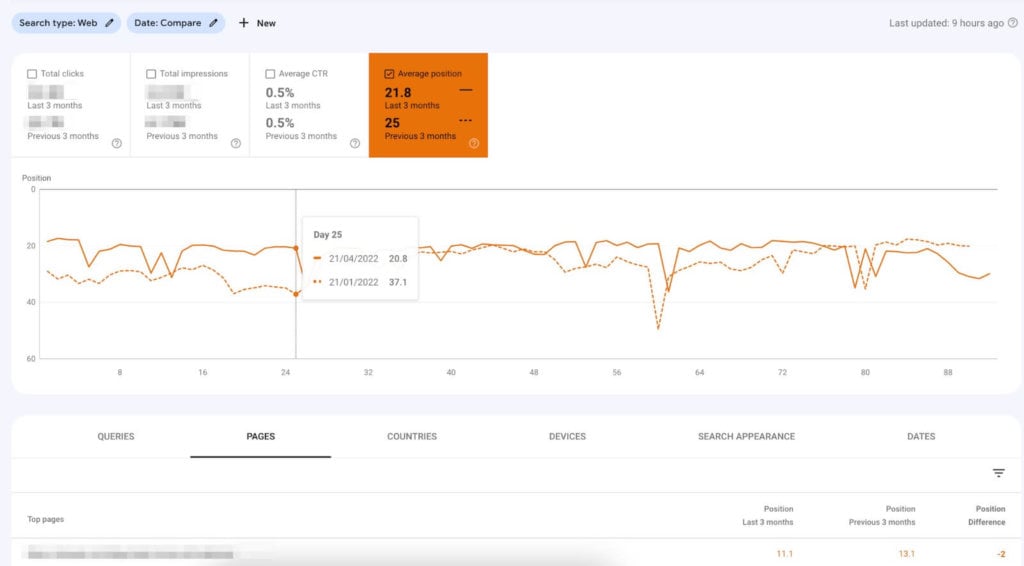
You can then make a spreadsheet of all the negatively affected pages and start looking for patterns as to what might be the cause.
But note it’s not enough to gather and analyze only your search results and analytics. You need a much larger sample to draw quality conclusions and take action.
That’s why you need to look at your direct search competitors.
Find out how they did in this update. What are the similarities and differences in your strategy compared to theirs?
Look at which pages gained or lost traffic and keywords and how they differ from yours. Note what they do differently, what they have that you don’t, and vice versa.
How to Prepare for the Next Google Core Algorithm Update
Once you have all the data and gather all the pages that are negatively affected, you can start changing your pages according to what you found out.
That includes working on your website’s content quality and authority, fixing any technical, on-page, and off-page SEO issues, and auditing your website for search intent, keywords, and relevancy.
• Ensure you are following Google general guidelines on broad core update
First, you must ensure that you are within Google’s webmaster guidelines regarding content creation.
This includes indexability, on-page elements like title and meta description, image size, and name. Implementing rich data, adding robots.txt file, auditing internal links, and the page loading speed is equally important.
Suppose you follow Google guidelines and make small changes to improve E-E-A-T, content quality, and user experience. In that case, your website can slowly pick up rankings and traffic even before the next Google core update, as stated by John Mueller in the Google Webmaster Central office-hours video.
• Implement Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) in your SEO strategy
Google has repeatedly emphasized the importance of E-E-A-T in SEO to all publishers and bloggers creating content. That has also been everything they say anyone can do to recover from an algorithm update–ensuring that you provide the best possible content for your readers.
This is especially important for Your Money or Your Life (YMYL) websites. They provide information, products, and services that impact the readers’ well-being, financial status, health, or security.
Therefore, YMYL websites must serve users with high-quality and trustworthy content, and, at the same time, they must convince Google that they are to be trusted.
But remember that a marketing strategy doesn’t only consist of quality content. Link-building, keyword research, page speed, and other SEO factors are equally important.
• Analyze changes in SERPs
Compare the keywords you used to rank for with websites now ranking for them instead of you. Then, try to figure out what those new websites were doing differently.
Things to look out for are the quality of content and search intent, backlink profiles, and on-page optimization. Then see what you can do to make your content better. That includes testing new titles and meta descriptions to increase the click-through rate (CTR).
8 Actionable Tips to Recover Lost Traffic
Here are some tips on what you can do right now to start recovering your traffic and keywords.
1. Update your existing content
One of the easiest things to start with is updating your articles with the latest information.
Add new data to the old posts, making them fresh and current again. For example, if there are recent statistics available–include them. If opinions have changed, reflect that in your article. Are there new, better ways of doing things?
Ensure your readers know that your content can keep up with the changes in the industry.
According to a Google update in 2011, the Caffeine update was a new web indexing system that allowed Google to crawl and store data more efficiently, improving its indexing rate and providing fresh results.
You can increase traffic to your existing pages by competing for new keywords and topics.
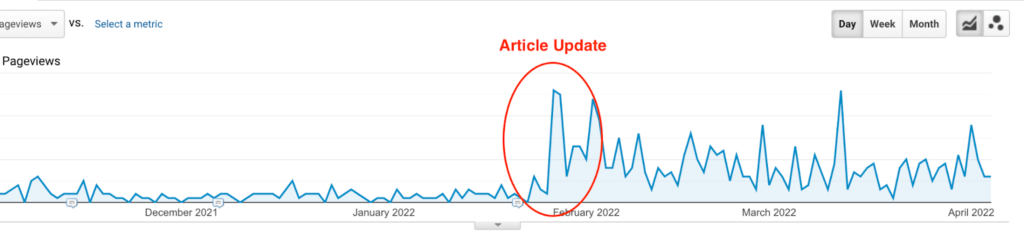
2. Audit your articles
By auditing your articles, you can ensure your content quality, relevancy, and search intent, providing the best experience for both–users and the Google algorithm. You need to look for things like keyword cannibalization issues and thin content.
Keyword cannibalization is when two or more pages target the same keyword with similar content. You make it harder for yourself to gain more traffic and outperform your competitors harder if you’re competing with yourself at the same time.
Review all the underperforming pages and look for keyword cannibalization. If you find any, you have 2 options on what to do:
- Consolidate both pages, create a more comprehensive article, and redirect the less valuable page to the newer content that better covers the topic.
- Combine all the pages into a brand new article.
Thin content is another issue that targets E-E-A-T principles and content quality. First, you need to do keyword and topic research for the pages where you have thin content. Then, find ways to improve them by adding new, relevant topics and keywords.
3. Work on your on-page SEO
You can make your content better and more accessible for readers and Google by improving your on-page SEO.
To do that:
- Ensure that all your images have a meta title
- Ensure that filenames reflect what the images are about
- Optimize titles, so they’re not too long or too short
- Resize your images to serve them faster to the readers
Make sure that you have a good URL structure for all your articles. Implement rich media that will enable you to compete for rich snippets in Google results and allow the Google bot to understand better what your page is all about.
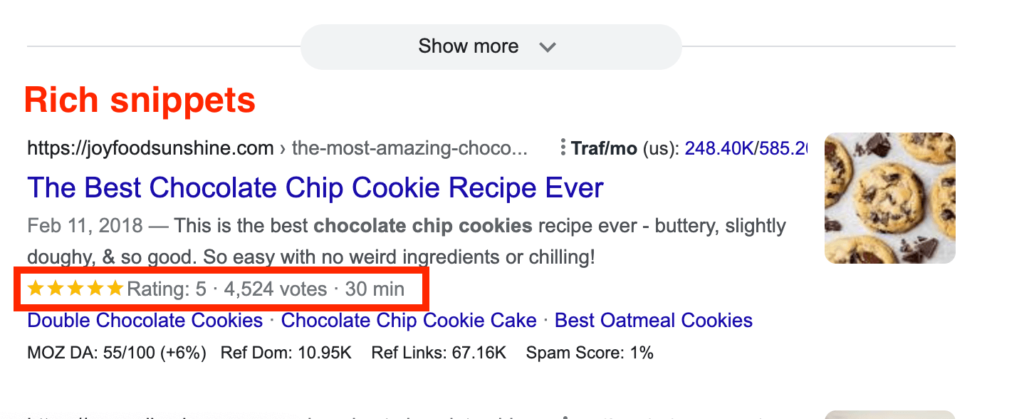
4. Create a consistent content strategy
To continue improving your content, create a consistent content strategy. Then, perform a competitor analysis by doing a content gap audit using tools like Ahrefs.
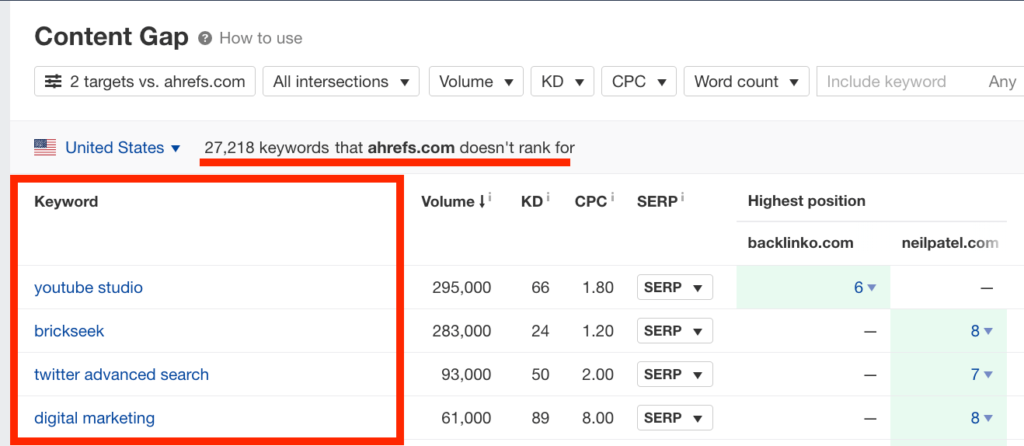
It will enable you to see what your competitors are writing about that you aren’t but should. Concentrate on your target audience’s interests and pain points.
Organize your articles in content clusters–it’s an excellent way to ensure you cover all the important subtopics of a larger topic.
Then, create a new content strategy to support your existing one and add topics you should write about.
5. Audit your internal links
Create an organized structure and approach for internal links strategy to promote related articles, create content hubs, and increase page rank.
A consistent internal linking strategy will also maximize your link-building efforts by ensuring that the benefits from incoming external links flow to your other pages.
Orphan pages are pages with no internal links pointing to them. As a result, they are hard to be discovered by readers or web crawlers. This prevents search engines from indexing the page and will not rank for your target keywords.
Use descriptive anchor texts when linking internally–the reader must understand where an internal link will lead them before they open it. And make sure all internal links lead to resources that expand or explain relevant topics.

Source: Setupad
6. Audit your backlink profile
Google Core updates don’t specifically target bad link profiles. However, a poor backlink profile still affects your website’s ranking in the SERPs. Therefore, keep an eye on your backlink profile and avoid low-quality backlinks.
Make sure you don’t have any spammy links linking to your website. Create and submit a disavow file to eliminate the links that may hurt your rankings and website health.
A disavow file is a text document you can submit to search engines, like Google, to invalidate links that you consider harmful to your website.
You can easily add a disavow file to your website using the Google Search Console tool for disavowing links. However, note that disavowing backlinks isn’t always the first step.
Google’s guidelines suggest that you should only use a disavow file on 2 occasions:
- You have a large number of low-quality, spam, or paid links leading to your website
- You have received a Google penalty – manual action.
Google has gotten quite savvy at evaluating if they should ignore a particular set of spammy links. For example, if a competitor performs a negative SEO attack on your website, most likely, Google will ignore these links.
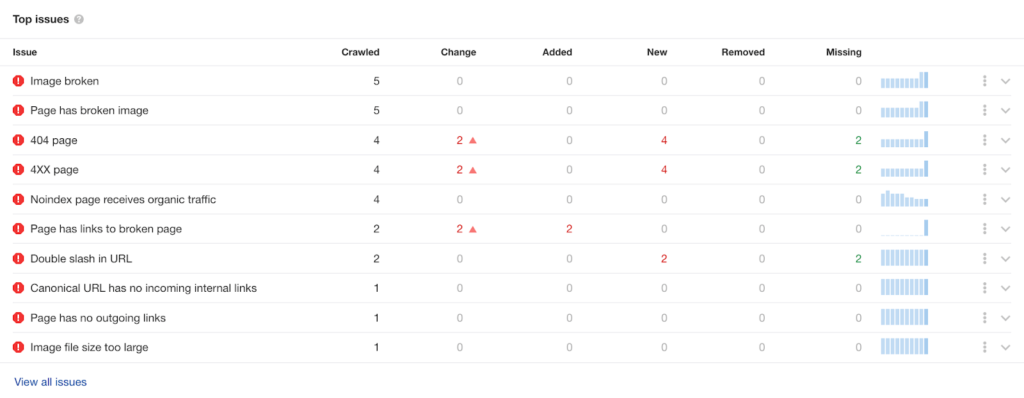
7. Do a technical audit of your website
A technical audit lets you know if there is anything wrong with your website, like broken links and 404 errors.
If a technical audit is too technical, you can use SEO tools like Ahrefs and MOZ. Both provide a free account where you can access some of the technical audit tools’ features.
But we suggest that to get a paid account for either one of these tools to be able to perform an in-depth audit.
Another option is hiring an SEO agency to do a full site audit. They will analyze how well your site performs in relation to Google’s requirements, taking into account on-page SEO, off-page SEO, and the technical health of your website.
Depending on your chosen service, you might receive instructions or suggestions on what to do with the report.
8. Work on your websites Core Web Vitals (CWV)
Google introduced Core Web Vitals (CWV) in 2020 to measure your website’s performance for each user. It measures 3 metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)–speed
- First input delay (FID)–responsiveness (note that this metric will be replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP) in March 2024)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)–visual stability
These three metrics are combined to measure the page experience of the user and are a confirmed ranking factor. You can check your CWV in your Search Console Core Web Vitals report page, Page Speed Insights, and Lighthouse report for Chrome users.
Although CWV might not directly impact how well your website will do in the following Google core update, it’s still essential for a good user experience on your website.
The user won’t be happy if your site is slow and unresponsive, and the page content constantly shifts. As a result, your click-through rates will drop, and so will the dwell time. And Google takes these into account when evaluating your website’s value.
Make sure you pass Core Web Vitals on both–mobile and desktop.
Conclusion
Google rarely provides actionable tips and suggestions for what publishers should do to recover from a Google core update. It also states that websites aren’t subjected to manual or algorithmic action. Instead, Google reassesses websites in order to provide a better experience for users.
But, if your website has lost traffic and keywords following a core update, it doesn’t mean that you should simply wait for the next update, hoping it would revert things to how they were.
Follow our tips and act now to prepare your site for the next update. Everything you do from this point on will go towards the well-being of your site for the following core update, which will likely happen in two or three months.


